More than three years after The King Arthur Conspiracy was published, the British media have been all over this story (representative sample from The Guardian).
Apparently, a research team from the University of Reading have concluded that the monks of Glastonbury made up the story that King Arthur was buried there, and an awful lot more besides.
I said as much in The King Arthur Conspiracy (and, incidentally, in The Grail, published earlier this year). So - vindicated!
Wonder what else the media will suddenly discover in the coming months, that I also wrote about a few years back ...
(Watch this space)
The Future of History
Showing posts with label Arthur. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Arthur. Show all posts
Tuesday, 24 November 2015
Monday, 20 April 2015
Review of "The Grail"
Well, there's already been an encouraging comment - I suppose you could call it an endorsement - on The Grail: Relic of an Ancient Religion from the all-round Arthurian expert John Matthews:
"A brisk rattle through the well-worn paths of the Grail and King Arthur. Some challenging new theories, applied with a kind of relish reminiscent of Robert Graves, make this a fascinating book."
I'd call that praise. And now, this new review has just been published on the Radical Goddess Thealogy blog.
Definitely worth a read!
"A brisk rattle through the well-worn paths of the Grail and King Arthur. Some challenging new theories, applied with a kind of relish reminiscent of Robert Graves, make this a fascinating book."
I'd call that praise. And now, this new review has just been published on the Radical Goddess Thealogy blog.
Definitely worth a read!
Sunday, 2 November 2014
Pagan Pages
Just been told that an interview with me is now up on the PaganPages.org website.
So, with thanks to Mabh Savage, I give you ... The Pagan Pages Interview with Author Simon Stirling. I think it's a good one.
Toodle-pip!
So, with thanks to Mabh Savage, I give you ... The Pagan Pages Interview with Author Simon Stirling. I think it's a good one.
Toodle-pip!
Labels:
Arthur,
Artuir mac Aedain,
Beltane,
Grail,
Gunpowder Plot,
Halloween,
King Arthur Conspiracy,
Moon Books,
Muirgein,
Myrddin Wyllt,
Scotland,
The History Press,
Who Killed William Shakespeare
Thursday, 2 October 2014
The Matter of Scotland
The Scottish Statesman, a new online newspaper for Scotland, launched today.
Here's my first contribution. It's about Arthur in Scotland, and the English approach to history.
More news to come ...
Here's my first contribution. It's about Arthur in Scotland, and the English approach to history.
More news to come ...
Tuesday, 19 August 2014
More About Arthur and Alyth
"Reekie Linn Waterfall, Angus" by stephen samson - Geograph http://www.geograph.org.uk/photo/765407. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Reekie_Linn_Waterfall,_Angus.jpg#mediaviewer/File:Reekie_Linn_Waterfall,_Angus.jpg
*
Not all of the ancient stories about, or inspired by, the historical Arthur use the familiar name of the hero. Two alternative titles or designations which recur in this context are: Bran ("Raven") and Llew (Welsh: "Lion") or Lleu (Welsh: "Light"), the latter also occurring as Lliw or Llyw (Welsh: "Leader"), possibly from the Irish luige, Welsh llw, an "oath".
So let's look at some of the stories which give one or other of these names to their oh-so Arthurian heroes.
Le Chevalier Bran
Among the earliest sources for the "battle of Circenn" in which Arthur died, the Irish Annals of Tigernach name Bran as one of the sons of Aedan, King of the Scots, who fell alongside Artur/Artuir. The Annals of Ulster name Bran instead of Arthur. Adomnan's Life of Columba names Arthur instead of Bran.
In Welsh legend, Bran, the "Blessed Raven", was the "crowned king of the Island of Britain" who fell through the treachery of an Irish king named Matholwch ("Prayer-Sort"). The final battle involved a marvellous cauldron of rebirth, which had been Bran's gift to Matholwch. Along with Bran, who had been fatally wounded by a poisoned spear, there were just seven survivors of this epic battle. There were also seven survivors of Arthur's last battle, according to the contemporary poet and eye-witness, Taliesin.
Meanwhile, the "Horn of Bran the Hard from the North" was one of the Thirteen Treasures of the Island of Britain ("which were in the North"), the other treasures having belonged to the contemporaries, relatives and near-neighbours of Arthur son of Aedan. A later tradition holds that Arthur had a hound called Bran. The name evolved into the "Brons" of Arthurian romance.
Bearing all that in mind, I was fascinated to come across an old Breton folksong entitled Le Chevalier Bran ou le Prisonnier de Guerre ("The Horseman Bran, or the Prisoner of War"). Published in 1842, this song begins:
A la battaile de Kerlouan
Fut blesse le chevalier Bran!
A Kerlouan, sur l'ocean,
Le petit fils de Bran le Grand!
Prisonnier, bien que victorieux,
Il dont franchir l'ocean bleu.
["At the battle of Kerlouan, the horseman Bran was wounded! At Kerlouan, by the sea, the grandson of Bran the Great! Captured, even though he was victorious, he was taken across the sea."]
There is much that can be said about this intriguing song, with its distinct Arthurian overtones - for example, the song tells of an oak-tree which stands in the field of battle, at the spot where "the Saxons were put to flight when Even suddenly appeared", Even probably being Owain (French "Yvain") who distinguished himself at Arthur's last battle, as we know from Aneirin's epic Y Gododdin poem.
However, for now we need only concentrate on two aspects of the Breton song. The first is that le chevalier Bran was the grandson of Bran le Grand. The grandfather of Arthur son of Aedan was Gabran, the Scottish king who gave his name to the region of Gowrie, in which Arthur's last battle was fought.
What, then, of Kerlouan, where the horseman Bran was wounded and taken away as a "prisoner of war"? At first glance, it appears to refer to the commune of Kerlouan in the Finisterre department of Brittany. But this place-name almost certainly travelled with the British refugees who fled to Armorica, the "Lesser Britain", when their Lothian homelands were conquered by the Northumbrian Angles in circa AD 638. The ker element is cognate with the Welsh caer, meaning a "castle", "stronghold" or "citadel". The louan element refers to St Elouan, otherwise Luan, Llywan, Lua, Lughaidh or Moluag ("My-Luan").
St Elouan or Louan was an obscure saint, said to have been contemporary with St Columba (and, therefore, with Arthur son of Aedan) and to have brought Christianity to the northern, Highland Picts, while Columba spread the Gospel among the southern, "Miathi" Picts (Arthur son of Aedan died, according to the Life of Columba, in "the battle of the Miathi").
The only place where St Elouan or Louan is still venerated as "Luan" is at Alyth, near the site of Arthur's last battle. The Church of St Luan now stands on Alexander Street. The Alyth Arches are all that remain of an earlier church, dedicated to St Luan, which supposedly occupies the site of an even earlier chapel. Alyth, then, has a strong claim to have been the "Stronghold of Luan" or Kerlouan where Arthur/le chevalier Bran was grievously wounded and carried away "across the sea". Any resemblance to the Caerleon which recurs in Arthurian tradition as an early form of Arthur's legendary court (later "Camelot") is probably not coincidental.
Llew Skilful Hand
Llywan is the Welsh form of Luan/Louan. In the ancient Welsh tale of Culhwch and Olwen (which, as I stated in my previous blog post, offers a potted account of Arthur's career, including the violent seizure of a magical cauldron), the treacherous king-turned-boar is finally driven into a river near Llyn Lliwan ("Lake Louan"), which was somewhere near Tawy (the Tay). This lake appears to be remembered on the map of the Alyth area as the Bankhead and Kings of Kinloch, adjacent to Arthurbank beside the River Isla. The marshy ground in the river's floodplain was once known, perhaps, as Loch Luan, a name preserved in the spot, near Meigle, known as Glenluie.
The name of this lake recalls Llew, Lleu or Lliw - as Aneirin sang in his Y Gododdin elegy for the northern warriors who fell in Arthur's last battle:
No one living will relate what befell
Lliw, what came about on Monday at the Lliwan lake.
Apart from the tales of his Irish counterpart, Lugh Long-Hand, the most famous of the British legends concerning Llew or Lleu is that found in the Welsh "Mabinogion", in which a great hero known as Llew Skilful Hand is tricked by his treacherous wife into standing on the edge of a cauldron by a riverbank, where he is speared by his wife's lover (the poisoned spear took a year to make because it could only be worked on during the Mass on Sundays). The name given for the river on the banks of which Llew was speared is "Cynfael".
Now, bear with me here. The bloody boar-hunt in the legend of Culhwch and Olwen which culminates with the destruction of the Boar-King in the river near Loch Tay and the "Lliwan lake" is, in fact, the second of two dangerous boar-hunts which took place "in the North". The first concerned another Boar-King - or, to be more accurate, another king of the Miathi Picts, who modelled their appearance on the boar, hence the Gaelic and Scots names for their territory in Angus: Circenn ("Comb-heads") and Camlann ("Comb-land"). The death of this previous Boar-King of the Miathi Picts can be dated to circa AD 580, some 14 years before the final battle.
His name was Galam, although he went by a couple of epithets. The Annals of Ulster record the death of "Cennaleth, king of the Picts" in 580. The Annals of Tigernach refer to the death of "Cennfhaeladh king of the Picts" in the year 578.
These epithets reveal the location of Galam's power-base in Angus as king of the Miathi Picts. Cennaleth translates as "Chief of Alyth". Cennfhaeladh could indicate a "Shaved-head", as in the boar tonsure sported by the Miathi warriors, or the chief of a "high, rounded hill", such as that which looms over the town of Alyth in the vale of Strathmore. The proper pronunciation of Cennfhaeladh would be "ken-eye-la". This suggests that the name of the River Isla, which flows past Alyth and Arthurbank, derives phonetically from Cennfhaeladh. It also suggests that the Cynfael river, on the bank of which Llew Skilful Hand was treacherously speared by his wife's adulterous lover, was really the Cennfhaeladh or River Isla, on the bank of which Arthur was mortally wounded.
Arthur and his men defeated Galam Cennaleth ("Chief-of-Alyth"), otherwise Cennfhaeladh, in about 580 at the "Battle of Badon" (Gaelic Badain, the "Tufted Ones"), fought a little further up the River Isla at Badandun Hill. Galam's Miathi warriors later joined forces with Arthur's nemesis, Morgan the Wealthy, and the final conflict was fought beneath Barry Hill and the Hill of Alyth, on the banks of the River Isla or "Cynfael".
Seekers of the Grail - which in its earliest form was a magical cauldron - might care to investigate the legend of "Sir James" and his cauldron of enlightenment, a legend centred on the Reekie Linn waterfall, behind the Hill of Alyth (see top of this post). It's quite an eye-opener.
Labels:
Aedan,
Alyth,
Arthur,
Arthurbank,
Badandun Hill,
Badon,
Bran,
Camelot,
Camlan,
Mabinogion,
Meigle,
St Columba,
Taliesin,
Y Gododdin
Sunday, 17 August 2014
Alyth, the Scene of Arthur's Last Battle
While I work on Shakespeare's Son - my biography of Sir William Davenant, a man of whom I'm becoming increasingly fond - The Grail continues to make its way through the publishing process, courtesy of Moon Books. So, by way of a sneak preview, in this post I shall offer up some of the evidence for the location of Arthur's last battle.
The Battle of Circenn
You probably think Arthur's last battle was fought at a place called "Camlann". I've been unable to find any reference to that place-name before the Middle Ages. The very earliest mentions of anyone called Arthur in the records indicate that he died in a battle fought in Angus, Scotland.
Adomnan of Iona's Life of Columba (circa 697) tells us that Artur son of Aedan was present when his father was "ordained" king of the Scots by St Columba in AD 574. The saint predicted the fates of Aedan's sons, announcing that Artur would "fall in battle, slain by enemies". Adomnan assured his readers that this prophecy came true when Artur and at least one of his brothers was killed in a "battle of the Miathi".
The Miathi, or Maeatae, were a Pictish tribe: essentially, they held the low-lying lands to the south and east of the Highland massif. Another Latinate term for these people was Verturiones.
The Irish annals, which drew at least some of their information from the records kept by Columba's monks on the Isle of Iona, specify that Artur son of Aedan died in a "battle of Circenn". This refers to the Pictish province which was roughly contiguous with today's Angus and the Mearns. The term Circenn combined the Gaelic cir, meaning a "comb" or "crest", and cenn, "heads". Circenn, then, was the land of the Comb-heads. This tells us that the Miathi Picts modelled their appearance on their totem beast, the boar (rather like their compatriots in the Orkneys, the Orcoi, from orc - a young boar). Indeed, it is possible that the Latinate name for the Verturiones tribe combines verres and turio and indicates the "offshoots" or "offspring" of the "boar", while the very term "Pict" (variant, "Pecti", "Pecht") quite possibly derived from the Latin pecten, a "comb".
Now, let's look at "Camlann" - the traditional name for Arthur's last battle. Its first appearance in the records comes in an entry interpolated into the Welsh Annals, where it refers to a gueith cam lann or "strife of cam lann". By the time this came to be written down, the region in which Artur son of Aedan died was speaking a version of Northumbrian Old English which became the dialect known as Lowland Scots. In that dialect, cam lann would mean "comb land".
In other words, "Camlann" is merely an anglicised version of the Gaelic Circenn, the land of the "Comb-heads" in which the first Arthur on record fell in a cataclysmic battle.
Culhwch and Olwen
One of the oldest of the Welsh (i.e. British) tales to feature Arthur is that of Culhwch ac Olwen. It forms a sort of mythologised, potted account of Arthur's career, culminating in the desperate and bloody hunt for a king who - for his sins - was turned into a boar. This hunt begins with a violent amphibious landing, at a site which can be identified as Cruden Bay, on the Aberdeenshire coast, after which Arthur is met by the "saints of Ireland" who "besought his protection". The dreadful Boar-King is challenged and chased from Esgeir Oerfel, the "Cold Ridge" of the Grampians, the Boar-King making his way across country towards Llwch Tawy (Loch Tay) before he is intercepted by Arthur and his men and driven into a river.
In The King Arthur Conspiracy I identified the treacherous Boar-King as Morgan the Wealthy, a renegade British prince who abducted Arthur's wife, Gwenhwyfar, and escaped into the land of the Miathi Picts (his bolt hole appears to have been the fortified Hill of Tillymorgan in Strathbogie). The site where Morgan finally came to grief is marked by the "Morganstone" on the west bank of the River Ericht, a short distance to the west of the Hill of Alyth in the great vale of Strathmore in Angus.
Arthurian Connections with Alyth
Before we proceed, let us consider some ancient references to Arthur and his family in the context of Alyth and its immediate vicinity.
In addition to having a son named Artur or Artuir, King Aedan of the Scots had a daughter called Muirgein. According to Whitley Stokes, editing and translating the Martyrology of a 9th-century Irish monk called Oengus, Muirgein daughter of Aedan was born "in Bealach Gabrain".
The inability of certain scholars to find a "Bealach Gabrain" in Scotland has led some to argue that Muirgein daughter of Aedan was utterly unconnected with Artur son of Aedan. But place-names evolve. The Gaelic term bealach, meaning a "pass" or "gorge", usually appears as "Balloch" on today's maps. There is a "Balloch" which runs along the feet of Barry Hill and the adjacent Hill of Alyth in Strathmore.
Furthermore, this "Balloch" or bealach was in a region named after the grandfather of Artur and Muirgein. Gabran was the father of Aedan. He ruled the Scots for twenty years until his death in about AD 559 and gave his name to the region of Gowrie (a corruption of Gabran). The "Balloch" near Alyth was in Gabran's land (Gabrain) and lies close to the town of Blairgowrie, which also recalls the name of Arthur's grandfather. The "Balloch" at the foot of the Hill of Alyth was almost certainly the "Bealach Gabrain" or "pass of Gowrie" where Arthur's (half-)sister, Muirgein daughter of Aedan mac Gabrain, was born. To pretend that the Balloch of Gowrie could not have been "Bealach Gabrain" because they are not spelled the same way these days is tantamount to claiming that Londinium and London could not have been the same place.
So Arthur's sister, Muirgein (latterly, Morgan le Fay), was born near Alyth. Writing in about 1527, the Scottish historian Hector Boece also indicated that Arthur's wife was buried at Meigle, which is just a mile or two south of Alyth. Hector Boece's local tradition recalled Gwenhwyfar as Vanora (via Guanora) and claimed that she had been held hostage in the Iron Age hill-fort atop Barry Hill, adjacent to the Hill of Alyth, before she was executed and buried in what is now the kirkyard at Meigle. A carved Pictish standing stone, now on display at the Meigle museum, reputedly depicts the execution or burial of Arthur's wife.
Y Gododdin
One of the best sources of information about Arthur's last battle is the ancient epic, Y Gododdin. This was composed and sung by Aneirin, a British bard of the Old North, and can be dated to circa AD 600 (the date of Arthur's last battle is given in the Irish annals as, variously, AD 594 and 596).
Unfortunately, the relevance of Aneirin's elegiac tribute to the warriors of Lothian (the "Gododdin") has been missed by scholars who want to believe that the poem bemoans the destruction of a British war-band from the Edinburgh area which had the misfortune to be wiped out at a mythical battle fought at Catterick in North Yorkshire. No evidence exists that any such battle was fought. The Angles (forerunners of the English) preferred not to recollect their defeats but were happy to remember, and to boast about, their victories. If the Angles of Northumbria had indeed obliterated a British band of heroes from Lothian at Catterick, we might assume that they would have remembered doing so. And no scholar has yet explained the presence of "Irishman and Picts" at this imaginary battle in Anglian territory.
A verse or two of Y G[ododdin, added at a later date than the original composition, described a battle fought in Scotland (Strathcarron) in AD 642 and the death in that battle of a Scottish king who just happened to be a nephew of Artur son of Aedan. This interpolation does at least suggest that the subject of the original poem was a battle fought in roughly the same area (Scotland) by the family of Artur and his father Aedan. The Y Gododdin poem also mentions various famous warriors who appear in the early accounts of Arthur's career and who were contemporary with Artur son of Aedan.
One surviving version of Y Gododdin even mentions Artur/Artuir by name:
Gochore brein du ar uur
caer ceni bei ef Arthur
rug ciuin uerthi ig disur ...
Confused by the misidentification of the battle sung about by Aneirin in Y Gododdin, and the assumption that Arthur himself could not have been present at that battle, scholars have persistently mistranslated this verse - mostly in an attempt to render the second half of the second line, "He was no Arthur". But Aneirin's verse should properly be translated thus:
Black ravens [warriors] sang in praise of the hero [Welsh, arwr]
of Circenn [transliterated into Welsh as "caer ceni"]. He blamed Arthur;
the dogs cursed in return for our wailing/lamentation ...
Aneirin indicated, in his Y Gododdin elegy, precisely where the final battle took place:
Eil with gwelydeint amallet
y gat veirch ae seirch greulet
bit en anysgoget bit get ...
Which translates as:
Again they came into view around the alled,
the battle-horses and the bloody armour,
still steadfast, still united ...
The "alled" was Aneirin's Welsh-language attempt at the Gaelic Allaid - also Ailt - or the Hill of Alyth.
Breuddwyd Rhonabwy
The extraordinary medieval Welsh tale of The Dream of Rhonabwy actually provides a description of the scene in the hours before Arthur's last battle was fought. The visionary seer, Rhonabwy, finds himself crossing a great plain with a river running through it (Strathmore). He is met by a character call Iddog, "Churn of Britain", who admits that it was he who caused the cataclysmic "battle of Camlan" by betraying Arthur. In company with Iddog, Rhonabwy approaches the "Ford of the Cross" (Rhyd-y-Groes) on the river. A great army is encamped on either side of the road and Arthur is seated on a little flat islet in the river, beside the ford.
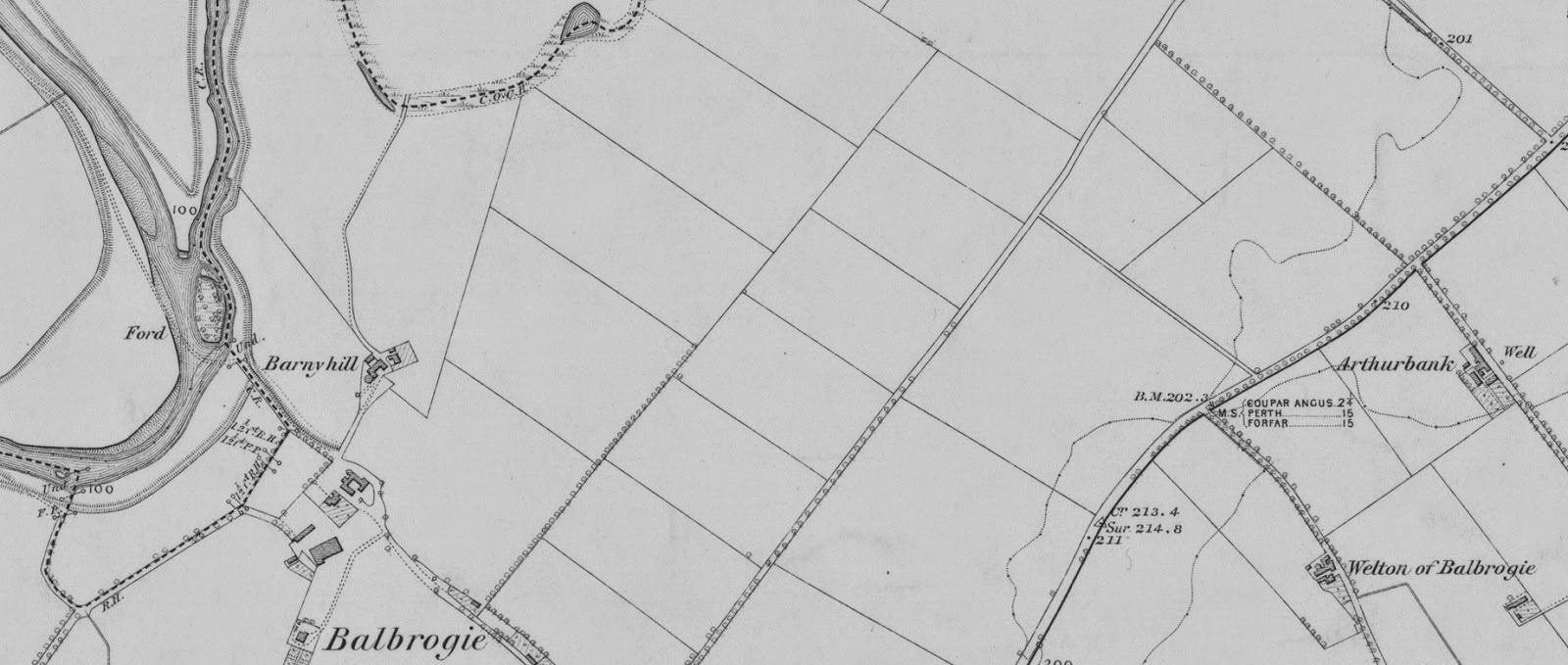
The topography precisely matches the detail from a 19th-century Ordnance Survey map of the area around Alyth seen at the top of this post. On the right-hand side of the detail is the ridge known as Arthurbank, which lies along the River Isla, opposite the junction of the River Ericht with the River Isla (a few miles down the Ericht from the site of the Morganstone). A little flat islet lies in the River Isla, close to the Arthurbank shore, and a ford runs alongside this little islet, exactly as described in the Welsh account of Rhonabwy's dream.
Aneirin also mentioned this ford in his Y Gododdin poem as rhyd benclwyd - the "ford" of the "grey" or "holy mount". There is, indeed, a Greymount marked on the map, a short distance to the north of the ford on the Isla. In his Agriculture of Perthshire, published in 1799, the Rev. Dr Robertson described the discovery of a "large Druidical temple" at Coupar Grange, adjacent to this ford. A standing stone found in this "temple" would no doubt have been rebranded a "cross" by the early Christians, so that the ford across the Isla, beside the little flat islet, would have become known as the Ford of the Cross (Rhyd-y-Groes), as described in The Dream of Rhonabwy, or the "Ford of the Grey/Holy Mount" (rhyd benclwyd) as described by Aneirin.
Until the late 18th century, an Arthurstone stood at the south-eastern edge of the Arthurbank ridge (its presence is still marked on the map). This Arthurstone corresponds to the Morganstone, a few miles away up the River Ericht, and marks the spot where Arthur fell in his battle with the Boar-King of the Miathi Picts in the land of the "crested" Comb-heads, Camlann.
The Head of the Valley of Sorrow
After the battle, Arthur's wife Gwenhwyfar was executed and buried only a mile or so away at Meigle. The legend of Culhwch and Olwen (which, interestingly, features a treacherous individual identified as Grugyn, who also appears in Aneirin's Y Gododdin) tells us that, after the battle at the river with the dangerous Boar-King, Arthur and his heroes once more "set out for the North" to overcome a fearsome witch. She was found inside a cave at Penn Nant Gofid - the "Head of the Valley of Sorrow"- on "the confines of Hell" (which we can interpret as the edge of the territory controlled by those boar-like Miathi Picts). The Welsh gofid ("sorrow/trouble/affiction/grief") appears to have been something of a pun, for another Welsh word for sorrow or grief is alaeth (compare Ailt, Allaid and Alyth, the "Head of the Valley of Alyth" being the very hill on which Arthur's wife is rumoured to have been held prisoner before her execution and burial nearby at Meigle).
In the Welsh tale, this witch is known as Orddu (that is, Gorddu - "Very Black"). A similar legend from the Isle of Mull, whose Arthurian associations have been overlooked for far too long, names the troublesome wife as Corr-dhu ("Black-Crane").
We might also note that the 9th-century Welsh monk known as Nennius described a "wonder" of Scotland in the form of "a valley in Angus, in which shouting is heard every Monday night; Glend Ailbe is its name, and it is not known who makes this noise."
Nennius's Glend Ailbe seems to be a corruption of the Gaelic word for a valley (glen) and the River Isla, or perhaps the Allaid or Hill of Alyth, which dominates the vale of Strathmore. The mysterious shouting in this "Valley of Sorrow" was reputedly heard ever Monday night. And we know from Aneirin's eye-witness account of Arthur's last battle that it came to an end on a Monday.
This is just some of the evidence for Arthur having fallen in the vicinity of Alyth. There is plenty more to come in The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Religion - including descriptions of the Pictish symbol stones, found close to the site of that battle, which actually depict the Grail in use!
I'll let you know when the book is about to be published.
Monday, 2 June 2014
The Meaning of "Camlann"
I received a message from Moon Books today, telling me that the copyedited manuscript of The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Religion is ready for me to check.
It seems unlikely that the book will be available before the Scottish independence referendum in September. I'll be keeping a close eye on the referendum: the vote takes place the day before my 12th wedding anniversary, and having got married on the Isle of Iona to a woman who is half-Scottish, as well as having gone to university in Glasgow, my sympathies lie very much with the "YES" campaign.
I was also interested to note that Le Monde published this piece, indicating that the pro-independence campaign is gaining ground. The reporter had been in Alyth, Perthshire, to follow the debate. Alyth, as I revealed in The King Arthur Conspiracy, is where Arthur fought his last battle.
How do I know this? Lots of reasons, not least of all the fact that the place is name checked in a contemporary poem of the battle.
But wasn't Arthur's last battle fought at a place called Camlan?
Well, for a long while I wasn't so sure. Now, though, I know that it was - sort of - and I explain why in my forthcoming book on The Grail. But as that may not be out before the referendum, I hereby present this information as a gift to the "YES" campaign and in honour of a warrior who gave his life fighting for Scottish (and British) independence.
Many commentators refuse to accept that the place-name "Camlan" isn't Welsh. The fact that Camlan is the Gaelic name for the old Roman fortifications at Camelon, near Falkirk in central Scotland, means nothing to them. Arthur's "Camlan" was Welsh, and that's all it could have been.
Very silly - and utterly useless, in terms of trying to track down the site of that all-important battle. If it was a Welsh place-name, it would have meant something like "Crooked Valley", which really doesn't help us very much.
The first literary reference to "Camlann" comes in the Annales Cambriae ("Welsh Annals") which mention Gueith cam lann - the "Strife of Camlann". However, that reference cannot be traced back to an earlier date than the 10th century, hundreds of years after the time of Arthur. The contemporary sources make no mention of "Camlann", and so it may be that the name didn't come into use until many years after Arthur's last battle was fought there.
The earliest literary reference to anyone called Arthur concerns an individual named Artur mac Aedain. He was a son of Aedan mac Gabrain, who was "ordained" King of the Scots by St Columba in 574. Accounts of the ordination ceremony indicate that Arthur son of Aedan was present on that occasion, and that St Columba predicted that Arthur would not succeed his father to the Scottish throne but would "fall in battle, slain by enemies."
Those same accounts tell us that Columba's prophecy came true: Artur mac Aedain died in a "battle of the Miathi", which means that he was killed fighting the Picts of central Scotland.
The Irish Annals, which were compiled from notes made by the monks of Iona, inform us that the first recorded Arthur was killed in a "battle of Circenn", fought in about 594. Circenn was the Pictish province immediately to the north of the Tay estuary - broadly, Angus and the Mearns - which was indeed the territory of the "Miathi".
Circenn might have been Pictish territory, but the name of the province is Gaelic. It combines the word cir (meaning a "comb" or a "crest") and cenn, the genitive plural of a Gaelic noun meaning "head". An appropriate translation of Circenn would therefore be "Comb-heads".
The Miathi Picts, like their compatriots in the Orkneys, appear to have modelled their appearance on their totem animal, the boar. This meant that they shaved their heads in imitation of the boar's comb or crest - rather like the Mohawk tonsure, which we wrongly think of as a "Mohican". Indeed, whilst we assume that the term "Pict" derived from the Latin picti, meaning "painted" or "tattooed", there are grounds for suspecting that it was actually a corruption of pecten, the Latin for a "comb" (hence the Old Scots word Pecht, meaning "Pict").
So where does "Camlann" fit into all this?
After Arthur's death, much of southern and central Scotland was invaded by the Angles, those forerunners of the English. As a consequence, the Germanic language known as Northumbrian Old English was established in southern and central Scotland by the 7th century. It eventually became the dialect called Lowland Scots.
In the Scots dialect, came, kem and camb all meant "comb". And lan', laan and lann all meant "land".
The land in which Arthur's last battle had been fought - that is, the Pictish province of Angus - was soon speaking an early variant of the English language, or Lowland Scots. The fact that the Pictish province of Circenn was named after its "Comb-heads", those Miathi warriors who cut their hair to resemble a boar's comb or crest, meant that the place became known by its early English equivalent: "Comb-land" or Camlann.
This was not, of course, the name that Arthur and his warrior-poets would have used for the place. But then, the term "Camlann" didn't appear in any literary source for at least another three or four hundred years. By the time the Welsh annalist came to interpolate the "Camlann" entry into the Annales Cambriae, the location had become known by its Old English/Lowland Scots name. But that name was merely a variant of the older Gaelic name for the province - Circenn, or "Comb-heads".
And that is where the first recorded Arthur fell in battle, as St Columba had predicted. Not in England or Wales or Brittany, but in Angus in Scotland.
The province of the Pictish "Comb-heads". The region known as "Comb-land", cam lann.
It seems unlikely that the book will be available before the Scottish independence referendum in September. I'll be keeping a close eye on the referendum: the vote takes place the day before my 12th wedding anniversary, and having got married on the Isle of Iona to a woman who is half-Scottish, as well as having gone to university in Glasgow, my sympathies lie very much with the "YES" campaign.
I was also interested to note that Le Monde published this piece, indicating that the pro-independence campaign is gaining ground. The reporter had been in Alyth, Perthshire, to follow the debate. Alyth, as I revealed in The King Arthur Conspiracy, is where Arthur fought his last battle.
How do I know this? Lots of reasons, not least of all the fact that the place is name checked in a contemporary poem of the battle.
But wasn't Arthur's last battle fought at a place called Camlan?
Well, for a long while I wasn't so sure. Now, though, I know that it was - sort of - and I explain why in my forthcoming book on The Grail. But as that may not be out before the referendum, I hereby present this information as a gift to the "YES" campaign and in honour of a warrior who gave his life fighting for Scottish (and British) independence.
Many commentators refuse to accept that the place-name "Camlan" isn't Welsh. The fact that Camlan is the Gaelic name for the old Roman fortifications at Camelon, near Falkirk in central Scotland, means nothing to them. Arthur's "Camlan" was Welsh, and that's all it could have been.
Very silly - and utterly useless, in terms of trying to track down the site of that all-important battle. If it was a Welsh place-name, it would have meant something like "Crooked Valley", which really doesn't help us very much.
The first literary reference to "Camlann" comes in the Annales Cambriae ("Welsh Annals") which mention Gueith cam lann - the "Strife of Camlann". However, that reference cannot be traced back to an earlier date than the 10th century, hundreds of years after the time of Arthur. The contemporary sources make no mention of "Camlann", and so it may be that the name didn't come into use until many years after Arthur's last battle was fought there.
The earliest literary reference to anyone called Arthur concerns an individual named Artur mac Aedain. He was a son of Aedan mac Gabrain, who was "ordained" King of the Scots by St Columba in 574. Accounts of the ordination ceremony indicate that Arthur son of Aedan was present on that occasion, and that St Columba predicted that Arthur would not succeed his father to the Scottish throne but would "fall in battle, slain by enemies."
Those same accounts tell us that Columba's prophecy came true: Artur mac Aedain died in a "battle of the Miathi", which means that he was killed fighting the Picts of central Scotland.
The Irish Annals, which were compiled from notes made by the monks of Iona, inform us that the first recorded Arthur was killed in a "battle of Circenn", fought in about 594. Circenn was the Pictish province immediately to the north of the Tay estuary - broadly, Angus and the Mearns - which was indeed the territory of the "Miathi".
Circenn might have been Pictish territory, but the name of the province is Gaelic. It combines the word cir (meaning a "comb" or a "crest") and cenn, the genitive plural of a Gaelic noun meaning "head". An appropriate translation of Circenn would therefore be "Comb-heads".
The Miathi Picts, like their compatriots in the Orkneys, appear to have modelled their appearance on their totem animal, the boar. This meant that they shaved their heads in imitation of the boar's comb or crest - rather like the Mohawk tonsure, which we wrongly think of as a "Mohican". Indeed, whilst we assume that the term "Pict" derived from the Latin picti, meaning "painted" or "tattooed", there are grounds for suspecting that it was actually a corruption of pecten, the Latin for a "comb" (hence the Old Scots word Pecht, meaning "Pict").
So where does "Camlann" fit into all this?
After Arthur's death, much of southern and central Scotland was invaded by the Angles, those forerunners of the English. As a consequence, the Germanic language known as Northumbrian Old English was established in southern and central Scotland by the 7th century. It eventually became the dialect called Lowland Scots.
In the Scots dialect, came, kem and camb all meant "comb". And lan', laan and lann all meant "land".
The land in which Arthur's last battle had been fought - that is, the Pictish province of Angus - was soon speaking an early variant of the English language, or Lowland Scots. The fact that the Pictish province of Circenn was named after its "Comb-heads", those Miathi warriors who cut their hair to resemble a boar's comb or crest, meant that the place became known by its early English equivalent: "Comb-land" or Camlann.
This was not, of course, the name that Arthur and his warrior-poets would have used for the place. But then, the term "Camlann" didn't appear in any literary source for at least another three or four hundred years. By the time the Welsh annalist came to interpolate the "Camlann" entry into the Annales Cambriae, the location had become known by its Old English/Lowland Scots name. But that name was merely a variant of the older Gaelic name for the province - Circenn, or "Comb-heads".
And that is where the first recorded Arthur fell in battle, as St Columba had predicted. Not in England or Wales or Brittany, but in Angus in Scotland.
The province of the Pictish "Comb-heads". The region known as "Comb-land", cam lann.
Monday, 17 March 2014
My Writing Process (blog tour)
I was "tagged" to take part in this blog hop by the wonderful Margaret Skea, whom I have known since the Authonomy days, and who posted about her writing process on her own blog last week.
Margaret passed on to me the four questions that writers are invited to answer as part of this blog tour.
So, here goes ...
1. What am I working on?
Right now, I'm finishing one project and starting another. The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Tradition has been occupying my time now since January 2013. I was looking to do something of a follow up to The King Arthur Conspiracy, partly because I had been doing some more research - especially into the location and circumstances of Arthur's last battle - and partly because I wanted to address some of the (very minor) objections to Artuir mac Aedain having been the original Arthur of legend.
Thanks to Trevor Greenfield of Moon Books, I was given the opportunity to write The Grail in an unusual way. Each month, from January to December 2013, I would write a chapter, which would then by uploaded onto the Moon Books blog. That meant that, each month, I would send my draft chapter to my associate, John Gist, in New Mexico, who would read it and comment on it for me, and I would visit my friend Lloyd Canning, a local up-and-coming artist, to discuss the illustration that would accompany the chapter. There would be a final rewrite, and then I'd submit the chapter and the image to Trevor at Moon Books.
It was a long process, and an odd one (I wouldn't normally submit anything less than a complete manuscript). I've spent the last couple of months revising the full text and adding a few more illustrations. And, well, it's about finished. John contacted me from the States last night to say that he had read through one of the more recent drafts of the full thing and he really liked it. It's not all about the distant past - there's a lot about how our brains work, and how a certain type of mind tends to ruin history (and other things) for everybody else. That type of mindset seeks to prevent research into figures like Artuir mac Aedain so that the prevailing myth can be maintained. The same type of mindset will cause us no end of problems in the immediate future, and the book ends with something of a prediction.
Coming up ... Sir William Davenant. I published a piece on The History Vault, a couple of days ago, about Shakespeare's Dark Lady. It could be read as a sort of introduction to my biography of Sir William Davenant. I've only just signed the contract for the Davenant book, and it's due to be handed in to The History Press in June 2015.
2. How does my work differ from others of its genre?
History for me is an investigative process. I lose patience very quickly with historians who do nothing more than repeat what the last historian said. It's a major problem: a consensus arises, and woe betide any self-respecting historian who challenges that consensus. But the consensus is often based, not on historical facts, but on a kind of political outlook. It tends to be history-as-we-would-like-it-to-be, rather than history-as-it-was.
There are similarities with archaeology. Dig down anywhere within the Roman walls of the old city of London and you'll hit a layer of dark earth. This was left behind by Boudica when she and her Iceni warriors destroyed Londinium in about AD 60. But if you don't dig down far enough, you won't find that layer.
Too much history - certainly where Arthur (and the Grail) and Shakespeare (and Davenant) are concerned - gets down as far as one layer and stays there. In the case of Arthur, that layer is the 12th century; with Shakespeare, it's the late 18th century. In both instances, that's when the story changed. New versions of Arthur and Shakespeare arose, reflecting the obsessions of the particular era. When historians dig down to that layer, and report on what they've found, they're not writing about Arthur or Shakespeare - they're writing about what later generations wanted to think about Arthur and Shakespeare.
You have to go down further. Otherwise, you're just repeating propaganda.
I'm also a bit fussy about how my books read. That's my dramatist background, I reckon. But I read a great many books - history, mostly, of course - and too many of them are, frankly, boring. I seek to write exciting, accessible history that has been more diligently researched than the norm. I don't seek to shock, but real history often is shocking. Maybe that's why so many historians prefer to keep telling the "consensus" story.
3. Why do I write what I do?
The work I do now started because I was intrigued and inquisitive. The familiar legends of Arthur are all well and good, but I was more interested in the man who inspired them - who was he? what made him so special? And the same with Shakespeare - how did a Warwickshire lad become the greatest writer in the English language? (My own background is not too different from Shakespeare's.) And what was the inspiration for the character of Lady Macbeth.
I'm still intrigued and inquisitive, but over the years I've found myself more and more determined to see justice done - to right the wrongs of the past. Those wrongs are perpetuated by historians who don't ask questions. And that's a betrayal, not only of the actual subjects (Arthur, Shakespeare) but also of the reader today. It's a kind of cover-up, designed - I believe - to reshape the past so that it justifies certain policies today. If you're a monarchist, for example, or an old-fashioned imperialist, you're going to want to believe that Queen Elizabeth I was marvellous. And then you're going to have to believe that Shakespeare thought she was marvellous. Which means that you'll have to turn a blind eye to what was going on during her reign, and to the criticisms which Shakespeare voiced. Before you know it, you're ignoring the facts altogether in order to write a history that supports your own prejudices. I can't believe how often that happens.
Both Arthur and Shakespeare were killed, and their stories were subsequently written up by their enemies. Their real stories are much more interesting - and they deserve to be told. If we cling to the myths, we allow demagogues to dictate our history to us.
4. How does my writing process work?
Well, it's not quick. The research can take years. Then there are usually a number of false starts. Fortunately, I tend to have some sort of agreement with a publisher, these days, so when I say I'm going to write something, that means I have to get on with it.
I'll start at the beginning, with the long, slow process of getting words down on the page (it's long and slow because I have to go hunting for the information before I put it down). But I always have a carefully worked out structure in my mind, and day after day a kind of rough draft takes shape. It's usually fairly messy, and at some point I'll stop and go back to the start, smartening it up and giving myself enough momentum to plough on and get a few more chapters drafted.
After that, it's an ongoing process of revision (never less than three drafts). For several months, I'll be revising the early chapters while I'm still drafting the later ones.
I have to work pretty much every day. For a finished manuscript of, say, 100,000 words, I'll expect to write anything up to 500,000 words, which will be sifted and boiled down to fit the appropriate length. I'll keep going back and revising different sections, here and there, and often, in the latter stages, I'll rewrite the chapters out of sequence (partly to keep them all fresh). Then there's endless, obsessive tinkering, as I fuss over every full stop and comma.
The King Arthur Conspiracy took seven months to write (and rewrite). Who Killed William Shakespeare? took nine months, and then some for the illustrations. The Grail took me a year to write (a chapter a month) and another 2-3 months to revise (with illustrations). With Sir William Davenant I want to create something special, so that'll take ages.
There are two things I couldn't do without. One is coffee. The other is my fantastically loyal, supportive and organised wife, Kim.
*****
I now get to tag a couple of authors who will pick up the baton and run with it, and I've chosen two great writers who are part of the Review Group on Facebook. I'll let the first introduce herself:
I’m Louise Rule, my first book Future Confronted was published in December 2013, and I am now researching my next book, the story of which will take me travelling from Scotland to England, and then to Italy. I am on the Admin Team of the Facebook group The Review Blog which I enjoy immensely.
Louise's blog can be found here.
My other chosen successor on this blog tour is Stuart S. Laing. Stuart writes about Scottish history - his posts on the Review Group Blog covering fascinating moments in Edinburgh's past are a joy to read, but it's his historical novels - the Robert Young of Newbiggin Mysteries - which really deserve attention.
Stuart's blog can be found here.
Finally, it remains for me only to thank Margaret Skea for inviting me to take part in this hop. And to thank you, dear reader, for perusing my musings.
Ciao!
Margaret passed on to me the four questions that writers are invited to answer as part of this blog tour.
So, here goes ...
1. What am I working on?
Right now, I'm finishing one project and starting another. The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Tradition has been occupying my time now since January 2013. I was looking to do something of a follow up to The King Arthur Conspiracy, partly because I had been doing some more research - especially into the location and circumstances of Arthur's last battle - and partly because I wanted to address some of the (very minor) objections to Artuir mac Aedain having been the original Arthur of legend.
Thanks to Trevor Greenfield of Moon Books, I was given the opportunity to write The Grail in an unusual way. Each month, from January to December 2013, I would write a chapter, which would then by uploaded onto the Moon Books blog. That meant that, each month, I would send my draft chapter to my associate, John Gist, in New Mexico, who would read it and comment on it for me, and I would visit my friend Lloyd Canning, a local up-and-coming artist, to discuss the illustration that would accompany the chapter. There would be a final rewrite, and then I'd submit the chapter and the image to Trevor at Moon Books.
It was a long process, and an odd one (I wouldn't normally submit anything less than a complete manuscript). I've spent the last couple of months revising the full text and adding a few more illustrations. And, well, it's about finished. John contacted me from the States last night to say that he had read through one of the more recent drafts of the full thing and he really liked it. It's not all about the distant past - there's a lot about how our brains work, and how a certain type of mind tends to ruin history (and other things) for everybody else. That type of mindset seeks to prevent research into figures like Artuir mac Aedain so that the prevailing myth can be maintained. The same type of mindset will cause us no end of problems in the immediate future, and the book ends with something of a prediction.
Coming up ... Sir William Davenant. I published a piece on The History Vault, a couple of days ago, about Shakespeare's Dark Lady. It could be read as a sort of introduction to my biography of Sir William Davenant. I've only just signed the contract for the Davenant book, and it's due to be handed in to The History Press in June 2015.
2. How does my work differ from others of its genre?
History for me is an investigative process. I lose patience very quickly with historians who do nothing more than repeat what the last historian said. It's a major problem: a consensus arises, and woe betide any self-respecting historian who challenges that consensus. But the consensus is often based, not on historical facts, but on a kind of political outlook. It tends to be history-as-we-would-like-it-to-be, rather than history-as-it-was.
There are similarities with archaeology. Dig down anywhere within the Roman walls of the old city of London and you'll hit a layer of dark earth. This was left behind by Boudica when she and her Iceni warriors destroyed Londinium in about AD 60. But if you don't dig down far enough, you won't find that layer.
Too much history - certainly where Arthur (and the Grail) and Shakespeare (and Davenant) are concerned - gets down as far as one layer and stays there. In the case of Arthur, that layer is the 12th century; with Shakespeare, it's the late 18th century. In both instances, that's when the story changed. New versions of Arthur and Shakespeare arose, reflecting the obsessions of the particular era. When historians dig down to that layer, and report on what they've found, they're not writing about Arthur or Shakespeare - they're writing about what later generations wanted to think about Arthur and Shakespeare.
You have to go down further. Otherwise, you're just repeating propaganda.
I'm also a bit fussy about how my books read. That's my dramatist background, I reckon. But I read a great many books - history, mostly, of course - and too many of them are, frankly, boring. I seek to write exciting, accessible history that has been more diligently researched than the norm. I don't seek to shock, but real history often is shocking. Maybe that's why so many historians prefer to keep telling the "consensus" story.
3. Why do I write what I do?
The work I do now started because I was intrigued and inquisitive. The familiar legends of Arthur are all well and good, but I was more interested in the man who inspired them - who was he? what made him so special? And the same with Shakespeare - how did a Warwickshire lad become the greatest writer in the English language? (My own background is not too different from Shakespeare's.) And what was the inspiration for the character of Lady Macbeth.
I'm still intrigued and inquisitive, but over the years I've found myself more and more determined to see justice done - to right the wrongs of the past. Those wrongs are perpetuated by historians who don't ask questions. And that's a betrayal, not only of the actual subjects (Arthur, Shakespeare) but also of the reader today. It's a kind of cover-up, designed - I believe - to reshape the past so that it justifies certain policies today. If you're a monarchist, for example, or an old-fashioned imperialist, you're going to want to believe that Queen Elizabeth I was marvellous. And then you're going to have to believe that Shakespeare thought she was marvellous. Which means that you'll have to turn a blind eye to what was going on during her reign, and to the criticisms which Shakespeare voiced. Before you know it, you're ignoring the facts altogether in order to write a history that supports your own prejudices. I can't believe how often that happens.
Both Arthur and Shakespeare were killed, and their stories were subsequently written up by their enemies. Their real stories are much more interesting - and they deserve to be told. If we cling to the myths, we allow demagogues to dictate our history to us.
4. How does my writing process work?
Well, it's not quick. The research can take years. Then there are usually a number of false starts. Fortunately, I tend to have some sort of agreement with a publisher, these days, so when I say I'm going to write something, that means I have to get on with it.
I'll start at the beginning, with the long, slow process of getting words down on the page (it's long and slow because I have to go hunting for the information before I put it down). But I always have a carefully worked out structure in my mind, and day after day a kind of rough draft takes shape. It's usually fairly messy, and at some point I'll stop and go back to the start, smartening it up and giving myself enough momentum to plough on and get a few more chapters drafted.
After that, it's an ongoing process of revision (never less than three drafts). For several months, I'll be revising the early chapters while I'm still drafting the later ones.
I have to work pretty much every day. For a finished manuscript of, say, 100,000 words, I'll expect to write anything up to 500,000 words, which will be sifted and boiled down to fit the appropriate length. I'll keep going back and revising different sections, here and there, and often, in the latter stages, I'll rewrite the chapters out of sequence (partly to keep them all fresh). Then there's endless, obsessive tinkering, as I fuss over every full stop and comma.
The King Arthur Conspiracy took seven months to write (and rewrite). Who Killed William Shakespeare? took nine months, and then some for the illustrations. The Grail took me a year to write (a chapter a month) and another 2-3 months to revise (with illustrations). With Sir William Davenant I want to create something special, so that'll take ages.
There are two things I couldn't do without. One is coffee. The other is my fantastically loyal, supportive and organised wife, Kim.
*****
I now get to tag a couple of authors who will pick up the baton and run with it, and I've chosen two great writers who are part of the Review Group on Facebook. I'll let the first introduce herself:
I’m Louise Rule, my first book Future Confronted was published in December 2013, and I am now researching my next book, the story of which will take me travelling from Scotland to England, and then to Italy. I am on the Admin Team of the Facebook group The Review Blog which I enjoy immensely.
Louise's blog can be found here.
My other chosen successor on this blog tour is Stuart S. Laing. Stuart writes about Scottish history - his posts on the Review Group Blog covering fascinating moments in Edinburgh's past are a joy to read, but it's his historical novels - the Robert Young of Newbiggin Mysteries - which really deserve attention.
Stuart's blog can be found here.
Finally, it remains for me only to thank Margaret Skea for inviting me to take part in this hop. And to thank you, dear reader, for perusing my musings.
Ciao!
Friday, 10 January 2014
A Race Against Time
I came across this press piece a few days ago. It's maybe not quite as bad as it first appears: nobody seems to be suggesting that we build new houses on top of the Old Oswestry hill-fort, only on the fields immediately adjacent. But what I found most interesting about the article is what it says of the 3,000 year old hill-fort - that Old Oswestry is "said to be the birthplace of Guinevere, King Arthur's Queen."Ooops, let's back up a bit there. "Guinevere" is a medieval invention. Or, rather, it's a Medieval French rendition of a Welsh name - Gwenhwyfar. It's just one of those Arthurian anomalies that we keep referring to the original characters by the wrong names. Forget Guinevere: she didn't exist. Let's call her Gwenhwyfar instead.
And while we're at it, let's stop saying "King Arthur", because he didn't exist either. His people remembered him as "the emperor Arthur". Or we could just call him "Arthur". But "King Arthur" is purely mythical, even though Arthur himself was real.
Anyway, there is a tradition - apparently - that Gwenhwyfar, the wife of Arthur the Emperor, was born at Old Oswestry. I was quite thrilled to read that, because in "The King Arthur Conspiracy" I endeavoured to trace Gwenhwyfar's family background, and was able to pin it down to the Flintshire region of North Wales. Oswestry, on the Welsh border, is just to the south of that part of the world, and was quite possibly part of the sub-kingdom ruled by Gwenhwyfar's father.
I identified Gwenhwyfar's father as Caradog Freichfras ("Strong-Arm"), who was initially associated with the kingdom of Glywysing, immediately to the south of Oswestry. However, along with a number of other Arthurian heroes, Caradog seems to have shifted his base of operations northwards, initially to the Tegeingl sub-kingdom of Gwynedd, immediately to the north of (and possibly incorporating) Oswestry.
The Iron Age hill-fort believed to have been Gwenhwyfar's birthplace is also pretty close to the parish of Llangollen. This was home to an individual who became known as St Collen, although I argue that he was better known as (St) Cadog - another princeling of South Wales who moved, first into North Wales and, later, into central Scotland. Cadog - or Collen - appears to have functioned as a foster-father figure to Gwenhwyfar, or perhaps as the Druidic leader of her maidenly cult, and it is rather telling to discover that a Croes Gwenhwyfar - "Gwenhwyfar's Cross" - exists at Llangollen.
In other words, there is a fair amount of evidence which places the young Gwenhwyfar in the general area of Oswestry - before she, like so many of the others, moved north into what is now Scotland - and so we cannot write off the possibility that she was indeed born in the Iron Age hill-fort of Old Oswestry.
But that's not really the point of this post. Neither, for that matter, is any hand-wringing or soul-searching over the desirability of a new housing estate next door to Gwenhwyfar's birthplace - although that issue might serve as a sort of metaphor for what this post is all about.
It's about the race against time that we're currently in. Let me explain:
We live in unprecendented times. The internet, for example, is like nothing humanity that has ever known. So much knowledge at our fingertips! Researching Arthur and his people - and, for example, narrowing down the location of his last battle, as I did in The King Arthur Conspiracy and, in more detail, in my forthcoming The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Religion - would have been immensely more time-consuming and expensive than it was.
However ... we also live in precedented times. I again cover this in The Grail, which is very much an exploration of the three "ages" of civilisation. We are currently being bullied out of the "Human age", which is characterised by liberal democracy and scientific materialism, by a resurgence of medieval "Heroic age" values, which we can characterise as dominated by religious fanaticism and extreme social inequality. This regression - the determination of some to tug us back into the kind of society which existed during the Middle Ages - is not really possible. It will lead (inevitably, I believe) to the collapse of our civilisation.
The internet is a fascinating product of our times. It is, in many ways, the ultimate "Human age" invention - possible only because of the technological infrastructure that was created by science, and thoroughly democratic, in that it is available to anybody. But the infrastructure necessary for the maintenance of a viable internet might not survive for long, and the anti-democratic instincts of those religious and political extremists who are forcing us back towards the "Heroic age" of times past are unlikely to favour the internet in its current form (although the internet is also one of the great purveyors of "Heroic age" thought, as uninformed opinion usurps the place of evidence-based logical reasoning and hysterical, paranoid memes spread like wildfire).
So, those of us who are fortunate enough to have access to the Global City which is the internet should really be using it to the best of our abilities. When it goes, it's gone - and our descendants will wonder at the race of supermen who could communicate instantaneously with millions across great distances, and who could access any information they required, just like that.
Do you really want your great-grandchildren to know that you had access to the greatest library the world has ever known, and the ability to exchange information with a massive global community - and all you did was post pictures of cats?
One of the ways in which the "Heroic age" is fighting back is through the rewriting of history. Michael Gove's cretinously empty-headed intervention in the matter of the First World War (which he seems to think was a rare old lark, sadly misreported ever since by "left-wing" academics and sit-com writers) shows that the religious-aristocractic view of the past, laced with ignorant flag-waving nationalism, is actively seeking to take control of history. Forget all those First World War poets who raged and railed against the hellish nightmare of the Western Front. No: a dimwitted politician now tells us that the war was a Good Thing, and anyone who questions that must be a "left-wing" radical.
In fact, the "Heroic age" has always rewritten history. It does so in order to cover its tracks and to pervert everyone's idea of the present. A government which is absolutely devoted to recreating the old aristocracy does not want you to think that the aristocratic officers of the First World War, or the aristocrats who sent so many millions to their deaths, were incompetent oafs. But the brainless attitude voiced by Michael Gove (Secretary of State for Education, would you believe?!) is symptomatic of a mindset that would happily send millions more to their deaths because they never learnt the lessons of history (how could they? Gove had already rewritten the book). And it's precisely that sort of thing that will undermine our civilisation.
Before we lose the internet, then - before we are banned from using it (because it's too democratic) or the infrastructure necessary to keep it going disintegrates (because it's "too expensive") - those of us who care about history really need to be making the most of our unprecedented opportunities to explore the past.
The "Heroic age" lied to us - repeatedly - about Arthur and his people. It was the "Heroic age" that invented the mythical "King Arthur" and changed the name of his wife from the authentic Gwenhwyfar to the familiar "Guinevere". And, let's face it, having lied to us before, it will lie to us again, given half a chance.
The only thing we can do is to uncover the historical truth, before the opportunity to do so is taken away from us. Arthur's last battle was fought at or near Alyth, in Scotland. A bit of determined research (internet and traditional) confirms this. But the "Heroic age" will have you believing that it happened somewhere else. Probably in the south. Evidence? Forget it. The "Heroic age" doesn't need evidence. It believes what it believes, and expects everyone else to believe it too. Evidence, be damned!
We could do our descendants a great big favour by using the internet intelligently, to challenge the foolish stories peddled by "Heroic age" propagandists. "King Arthur" never existed - he was an English invention - and the myth has always stood in the way of proper investigation. But tracing the historical Arthur is possible (and enjoyable), especially when we have all the resources of the internet at our command. Of course, the dogmatic voices of the "Heroic age" will shriek and shout and throw their little tantrums, but our great-grandchildren have the right to know what happened in the past. We have a duty to tell them, and not to let the past remain obliterated and re-engineered by fanatical demagogues, for whom everything must defend an extremist religious and/or political point-of-view.
So, in that sense, the story at the top of this post is a kind of metaphor. We are able - if we choose - to find out a great deal about Gwenhwyfar and her (possible) birthplace. But that won't last forever. Like the Iron Age hill-fort in which Arthur's wife was quite possibly born, there is a threat looming. The enemies of the truth are advancing.
There is still time to save the past from their bigoted opinions. But we do have to act.
Houses next door to Gwenhwyfar's birthplace? I'm not so worried about that, to be honest. Just so long as we succeed in uncovering and explaining who Gwenhwyfar was, while we still have the chance.
Friday, 20 December 2013
Five Facts About Arthur
Barry Hill, just north of Alyth in Angus, photographed by Richard Webb. Arthur's last battle was fought near here.
I've written quite a lot about prejudice, lately. This comes partly from my work on the final chapter for The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Religion, in which I analyse what makes people believe certain things - irrespective of, and often in direct contradiction of, the evidence.
Because the fact is that where a lot of history is concerned, prejudice dictates what we believe. Hence, the revelation that Arthur was Scottish (or perhaps it would be more accurate to say North British) is either ignored or derided by people who prefer to cling to the notion that he was, in some strange, anachronistic sort of way, essentially English.
A couple of posts back, I flirted with the idea of posting a handful of facts, none of which is in any way speculative, about Arthur. These indisputable facts point to one conclusion only - that the "King Arthur" we read about so often is a manufactured legend. The real Arthur was not a "king". He had no connection with southern Britain and was active somewhat later than the timeframe asserted by so many "experts".
So, here goes:
1. The earliest Arthur on record was northern.
Long before we encounter any English references to Arthur, a princely "Arthur" was written about. He was Artur mac Aedain ("Arthur son of Aedan"), whose father, Aedan mac Gabrain, was ordained as King of the Scots by St Columba in AD 574. The Life of Columba, written by Adomnan of Iona in about 697, drawing on earlier accounts written by previous abbots of Iona, suggests that Artur was present when his father Aedan was ordained. St Columba predicted that this Artur would never be king but would "fall in battle, slain by enemies". The Life of Columba goes on to confirm that Artur did indeed die in a "battle of the Miathi", the tribal name referring to the southern or Lowland Picts of central Scotland.
The Irish annals similarly indicate that Artur mac Aedain died fighting the Picts - his death in a "battle of Circenn" being dated to 594 (Annals of Tigernach). Circenn was the old Pictish province which corresponds with today's Angus and the Mearns, just north of the Tay estuary in Scotland.
Like Adomnan's Life of Columba, the Irish annals ultimately derived from the Isle of Iona, off the coast of Argyll in western Scotland. Key events were listed alongside the Easter Tables which allowed early monasteries to calculate the date of Easter each year; these events were later transcribed into the chronicles known as "annals". The source of the information regarding Artur's death in a battle against the Miathi Picts, fought in Circenn (Angus) in about 594, was therefore the monastery on Iona which had been established by St Columba - the very man who "ordained" Artur's father Aedan in 574.
Most accounts of Arthur's life avoid mentioning the Irish annals or the Life of Columba because they reveal that, long before there was any mention of Arthur in a southern or "English" context, the Irish or Scots had already established that an Arthur died fighting against the Picts in Angus. There are no surviving references to anyone named Arthur before these Irish accounts, which drew on contemporary references. Some scholars insist that Artur mac Aedain could not have been the "real" Arthur but must have been named after an earlier hero called Arthur. But the point needs to be made that no evidence whatsoever exists for anyone named Arthur before Artur mac Aedain.
2. The early British sources associate Arthur with the North.
No contemporary British accounts of Arthur survive, although we do have transcriptions of ancient poems and stories which were copied out in the Middle Ages. They all point to Arthur having been a northerner, who associated with northern princes of the late-6th century (that is, the lifetime of Artur mac Aedain).
Starting with Taliesin, who proudly called himself the "Primary Chief Bard" of Britain and who flourished in the late-6th century, we find repeated references to Arthur as a contemporary figure. For a while, at least, Taliesin was attached to the court of Urien, a king of North Rheged (Cumbria) who died in 590. By his own admission, Taliesin was also based at Edinburgh for some time. In addition to composing poems and elegies for Urien and his son Owain, Taliesin also praised Lleenog of Lennox (Loch Lomond) and his son Gwallog. He also sang a death-song for "Uthyr Pen" ("Uther the Chief") and an extraordinary account of Arthur's funeral (Preiddeu Annwn).
Equally, Aneirin - a princely bard of the North who flourished in the late-6th century - made mention of Arthur. Aneirin's masterpiece is known as Y Gododdin and sang of the warriors of Edinburgh and Lothian who perished in a military disaster fought shortly before the year 600. The earliest surviving version of Y Gododdin, written in an archaic form of Welsh, includes a direct reference to Arthur (we will return to this).
Moving onto the British stories of Arthur and his heroes, although these were transcribed by medieval monks during the Middle Ages, there is no good reason to presume that they were made up during that same period; rather, they almost certainly preserved a record which had been passed down orally by bards and storytellers. In these stories (some of which were edited and translated in the 19th century by Lady Charlotte Guest and published as the Mabinogion or "Tales of the Early Age"), Arthur is consistently presented in the company of northern individuals of the late-6th century.
Such individuals include Taliesin, Urien of North Rheged and his son Owain, Cynon son of Clydno of Edinburgh and Peredur of York (Taliesin, Owain and Cynon are among those named alongside Arthur in Aneirin's Y Gododdin poem of a northern battle fought in the late-6th century). These historical figures were later romanticised (Urien - Uriens; Owain = Yvain; Peredur = Perceval - compare Lleenog and Gwallog, who became the legendary father and son duo, Lancelot of the Lake and Galahad).
Others who appear to have accompanied Arthur on his forays "into the North" include St Cadog, one of Arthur's "four-and-twenty horsemen", who founded a monastery in central Scotland, and whose hagiography features several encounters with Arthur and other contemporary figures, such as Rhydderch of Dumbarton (died circa 614). Rhydderch, meanwhile, is repeatedly associated with the Merlin-figure, Myrddin Wyllt, who "went mad" at a battle fought in the Scottish Borders in 573 and then spent much of his time in the "Caledonian forest", where at least one of Arthur's battles was fought, according to a list compiled in about 829 by a Welsh monk commonly known as Nennius.
3. The early romances associate Arthur - and the Grail - with the North.
As early as 1120, Lambert, the canon of St Omer in Brittany, wrote of the "palace of the warrior Arthur" as being "in the land of the Picts" - or Scotland, as we would now know it. Lambert wrote in Latin, but used a Gaelic name for Arthur (Artuir militis).
Most mainstream accounts of "King Arthur" do not mention Lambert's testimony because it draws us away from the myth of the southern Arthur. That myth was forged by Geoffrey of Monmouth, whose account of Arthur's life and career formed part of his Historia Regum Britanniae or "History of the Kings of Britain", which he completed in about 1137. Geoffrey appears singlehandedly to have invented the legend of Arthur's birth at Tintagel in Cornwall. He also claimed that Merlin transported the "Giant's Dance" from Ireland by magic, bringing it to England where it became known as Stonehenge. Very few people take that claim seriously, and yet a surprising number are eager to take the equally unfounded story about Tintagel as Gospel. (In a later account, Geoffrey placed Merlin in the company of Taliesin, correctly identifying Myrddin Wyllt as the origin of the Merlin legend and a contemporary of the late-6th-century "Primary Chief Bard", but by then the damage had been done - those who wanted Arthur to have been "English" had the Tintagel myth to turn to, even though nobody before Geoffrey of Monmouth had mentioned it.)
Still, writers in Britain and on the Continent continued to link Arthur and his exploits with the North. Beroul, for example, whose verse romance of Tristan was composed in about 1200, stated unequivocally that Arthur and his Round Table were located at Stirling, on the River Forth in central Scotland. There was indeed a "Tristan" who was contemporary with Artur mac Aedain. His name was originally Pictish - Drust - but the Scots came to think of him as "St Drostan" and placed him in the company of St Columba (as "Drosten", he is named on a 9th-century Pictish stone at St Vigeans in Angus, not far from the scene of Artur's last battle; an early British account has "Drystan" fleeing with his lover, Esyllt, into the "Caledonian forest").
In Chretien de Troyes's version of the Peredur story - Perceval ou le conte du graal - the sword presented to the Grail knight by his uncle, the Fisher King, could only be "rehammered, retempered and repaired" at a lake beyond the River Forth. The Estoire del Saint Graal, composed in about 1230, stated that both Joseph of Arimathea, who supposedly brought the "Holy Grail" to Britain, and his son Josephus were buried in Scotland. At about the same time, one Guillaume le Clerc wrote his romance of Fergus, in which a young would-be knight encounters Arthur and his men in Galloway and then goes on a quest across much of Scotland. The Queste del Saint Graal (circa 1230) remarked that Celydoine, an ancestor of the knights Lancelot and Galahad, was "the first Christian king to hold sway over Scotland".
An oral tradition concerning Arthur continued in Scotland - and especially in the islands of the Hebrides - until the tales were finally written down in the 18th and 19th centuries. In one of these, which was recorded on the Isle of Tiree, very close to Iona, Arthur is "Chief Arthur son of Iuthar".
4. Arthur's enemies were northern.
Traditionally, Arthur fought against the Saxons, who colonised much of southern Britain in the 5th and 6th centuries AD. The term "Saxon" is still used in Welsh (Sais) and Scottish Gaelic (Sasunn) to designate an "Englishman" and "England" respectively. The term "England", however, derives not from the Saxons but from the Angles, who formed Engla land some time after they had established their kingdom of Northumberland.
The Angles did not lay claim to their first northern kingdom (Bryneich - or Bernicia, as the Angles called it) until about AD 547. They later added the kingdom of Deira (British Deywr) in 559, and together these adjacent territories on the coast of north-east England formed the Anglian kingdom of Northumberland. Forays were made into central Scotland (thus, Artur and his contemporaries fought them in Lennox, near Loch Lomomd, and at Craigmaddie Muir, north of Glasgow). By 590, though, an alliance of British and Irish chieftains had pretty much driven the Angles back into the sea. Only the treachery of a British petty-king, Morgan the Wealthy, whose power base was at the Edinburgh, caused the British resistance to collapse after the assassination of Urien of North Rheged.
Just five years later, the resurgent Angles overran much of the North. They finally conquered Edinburgh and Lothian in 638.
Between 590 and 595, or thereabouts, the invading "English" underwent an astonishing change of fortune - from being all-but wiped out in 590 to taking control of much of North Britain in 595.
Artur mac Aedain, we should remember, died in a battle fought in Angus in 594. During his lifetime, the Anglian threat had been contained, and almost eradicated, before an act of treachery led to the death of Arthur's companion, Urien, and then his own death opened the floodgates to the conquest of North Britain by the Angles. The historical circumstances therefore square with the later legends of Arthur: he sought to hold back the English, and was remarkably successful in doing so, until treachery struck. And with the death of Arthur, Britain was finished.
But the Angles were not his sole enemies. Geoffrey of Monmouth - who acknowledged that Arthur had fought battles around Dumbarton and Loch Lomond, a very long way from his supposed base in the south - also noted that there had been "Scots, Picts and Irish" ranged against Arthur in his final conflict, and that the various factions who had been brought into alliance by a treacherous British chieftain included both pagans and Christians. Geoffrey specifically stated that the "Saxons" were to be awarded with the land between the River Humber and Scotland - that is, Northumberland, the land of the Angles - in return for joining forces against Arthur.
5. Arthur's last battle was fought in the North.
We think of it as the "Battle of Camlann", and yet no contemporary references to any such battle survive. The last battle of Arthur doesn't appear to have been referred to as "Camlann" until the Middle Ages, when it was entered into the Annals of Wales as Gueith cam lann, the "Strife of Camlann".
It is usually assumed that "Camlann" is, and could only be, a Welsh place-name. This is not a reasonable assumption: the old Roman fort at Camelon, near Falkirk (just south of Stirling), is known as Camlan in Gaelic (Kemlin in Scots), and so we shouldn't suppose that cam lann was an authentic British (i.e. Brittonic) place-name.
In fact, the term cam lann translates via Anglo-Saxon - and via Lowland Scots, a derivative of the Old Germanic tongue spoken by the Angles, which had been established in southern Scotland by the 7th century - as "comb land".
Artur mac Aedain, we recall, died in 594 at a "battle of Circenn". The term circenn combines two Old Irish words, cir - meaning "comb" or "crest" - and cenn, meaning "heads". The Angus region, which was then known as Circenn, appears to have been the capital of the Miathi Picts, who seem to have modelled their appearance on the boar (Galam, a chief of the southern Picts who was almost certainly killed by Arthur in 580, bore two epithets: Cennaleth, or "Chief of Alyth", and Cennfaeladh, meaning "Shaved-Head"; he was also known as "Little-Boar", Welsh Baeddan, or "Little Tufted One", Gaelic Badan, since his head was shaved to represent the tuft, crest or "comb" of a boar).
So, Artur mac Aedain died in 594 in a battle in Circenn, the land of the "Comb-heads" or the boar-crested warriors of the Miathi Picts. His death more or less put an end to the British resistance to Anglian invasion.
The Arthur of legend died in a battle in "Comb land" or cam lann. His death more or less put an end to the British resistance to the "Saxons", or the English as they are now known.
With this in mind, we might return to the Y Gododdin poem of Aneirin, which sang of the heroes (many of them resident fixtures of the Arthurian legends) who fought so valiantly in a disastrous encounter with the Northumbrian Angles which took place not long before the year 600 and not all that far from Edinburgh. Indeed, Aneirin tells us where it happened:
Again they came into view around the Allaid,
The battle-horses and the bloody armour,
Still steadfast, still united ...
The "Allaid" (Gaelic Ailt) was the Hill of Alyth, above the River Isla in Strathmore, the great valley of Angus.
As previously stated, the earliest surviving version of Y Gododdin includes a reference to Arthur. This reference has been repeatedly mistranslated by scholars who do not want to think of Arthur as a northerner or to consider the possibility that Arthur might have been present at this disastrous battle between the Gododdin warriors of Lothian and the massed ranks of Angles, Scots, Irish and Picts. Here's the passage which mentions Arthur:
Gochore brein du ar uur
caer ceni bei ef arthur
rug ciuin uerthi ig disur ...
We can now translate this passage thus:
"Black ravens sang in praise of the hero
of Circenn. He blamed Arthur;
the dogs cursed in return for our wailing ..."
The "hero" (Welsh arwr) of "Circenn" (corrupted to caer and the genitive ceni in the transcription) was probably Arthur, who was blamed for his own death by his principle enemy whilst his black raven warriors sang their dirges over him.
As St Columba had predicted, he had "fallen in battle, slain by enemies". This battle was fought against a motley bunch of Angles, Scots, Picts and Irish, and it took place in the "comb land" (cam lann) of the "Comb-heads" (Circenn), where Arthur - surrounded by those very princes of North Britain who would follow him into the legends - was fatally wounded near the Allaid or "Hill of Alyth", the chief seat of Galam, the onetime boar-king of the Miathi.
This region is also known as Gowrie, after Gabran, the grandfather of Artur mac Aedain, who had annexed the territory in about 525. The place where Artur fell is known to this day as Arthurbank, the precise spot still being known as Arthurstone.
Southern Britain never had an Arthur, nor even a figure remotely like Artur mac Aedain.
The myth of the southern Arthur is exactly that - a myth.
The real Arthur, as all the available evidence indicates, was a northerner, active in the second half of the 6th century, and only blind prejudice stands in the way of our recognition of Artur mac Aedain as the hero he was.
I've written quite a lot about prejudice, lately. This comes partly from my work on the final chapter for The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Religion, in which I analyse what makes people believe certain things - irrespective of, and often in direct contradiction of, the evidence.
Because the fact is that where a lot of history is concerned, prejudice dictates what we believe. Hence, the revelation that Arthur was Scottish (or perhaps it would be more accurate to say North British) is either ignored or derided by people who prefer to cling to the notion that he was, in some strange, anachronistic sort of way, essentially English.
A couple of posts back, I flirted with the idea of posting a handful of facts, none of which is in any way speculative, about Arthur. These indisputable facts point to one conclusion only - that the "King Arthur" we read about so often is a manufactured legend. The real Arthur was not a "king". He had no connection with southern Britain and was active somewhat later than the timeframe asserted by so many "experts".
So, here goes:
1. The earliest Arthur on record was northern.
Long before we encounter any English references to Arthur, a princely "Arthur" was written about. He was Artur mac Aedain ("Arthur son of Aedan"), whose father, Aedan mac Gabrain, was ordained as King of the Scots by St Columba in AD 574. The Life of Columba, written by Adomnan of Iona in about 697, drawing on earlier accounts written by previous abbots of Iona, suggests that Artur was present when his father Aedan was ordained. St Columba predicted that this Artur would never be king but would "fall in battle, slain by enemies". The Life of Columba goes on to confirm that Artur did indeed die in a "battle of the Miathi", the tribal name referring to the southern or Lowland Picts of central Scotland.
The Irish annals similarly indicate that Artur mac Aedain died fighting the Picts - his death in a "battle of Circenn" being dated to 594 (Annals of Tigernach). Circenn was the old Pictish province which corresponds with today's Angus and the Mearns, just north of the Tay estuary in Scotland.
Like Adomnan's Life of Columba, the Irish annals ultimately derived from the Isle of Iona, off the coast of Argyll in western Scotland. Key events were listed alongside the Easter Tables which allowed early monasteries to calculate the date of Easter each year; these events were later transcribed into the chronicles known as "annals". The source of the information regarding Artur's death in a battle against the Miathi Picts, fought in Circenn (Angus) in about 594, was therefore the monastery on Iona which had been established by St Columba - the very man who "ordained" Artur's father Aedan in 574.
Most accounts of Arthur's life avoid mentioning the Irish annals or the Life of Columba because they reveal that, long before there was any mention of Arthur in a southern or "English" context, the Irish or Scots had already established that an Arthur died fighting against the Picts in Angus. There are no surviving references to anyone named Arthur before these Irish accounts, which drew on contemporary references. Some scholars insist that Artur mac Aedain could not have been the "real" Arthur but must have been named after an earlier hero called Arthur. But the point needs to be made that no evidence whatsoever exists for anyone named Arthur before Artur mac Aedain.
2. The early British sources associate Arthur with the North.
No contemporary British accounts of Arthur survive, although we do have transcriptions of ancient poems and stories which were copied out in the Middle Ages. They all point to Arthur having been a northerner, who associated with northern princes of the late-6th century (that is, the lifetime of Artur mac Aedain).
Starting with Taliesin, who proudly called himself the "Primary Chief Bard" of Britain and who flourished in the late-6th century, we find repeated references to Arthur as a contemporary figure. For a while, at least, Taliesin was attached to the court of Urien, a king of North Rheged (Cumbria) who died in 590. By his own admission, Taliesin was also based at Edinburgh for some time. In addition to composing poems and elegies for Urien and his son Owain, Taliesin also praised Lleenog of Lennox (Loch Lomond) and his son Gwallog. He also sang a death-song for "Uthyr Pen" ("Uther the Chief") and an extraordinary account of Arthur's funeral (Preiddeu Annwn).
Equally, Aneirin - a princely bard of the North who flourished in the late-6th century - made mention of Arthur. Aneirin's masterpiece is known as Y Gododdin and sang of the warriors of Edinburgh and Lothian who perished in a military disaster fought shortly before the year 600. The earliest surviving version of Y Gododdin, written in an archaic form of Welsh, includes a direct reference to Arthur (we will return to this).
Moving onto the British stories of Arthur and his heroes, although these were transcribed by medieval monks during the Middle Ages, there is no good reason to presume that they were made up during that same period; rather, they almost certainly preserved a record which had been passed down orally by bards and storytellers. In these stories (some of which were edited and translated in the 19th century by Lady Charlotte Guest and published as the Mabinogion or "Tales of the Early Age"), Arthur is consistently presented in the company of northern individuals of the late-6th century.
Such individuals include Taliesin, Urien of North Rheged and his son Owain, Cynon son of Clydno of Edinburgh and Peredur of York (Taliesin, Owain and Cynon are among those named alongside Arthur in Aneirin's Y Gododdin poem of a northern battle fought in the late-6th century). These historical figures were later romanticised (Urien - Uriens; Owain = Yvain; Peredur = Perceval - compare Lleenog and Gwallog, who became the legendary father and son duo, Lancelot of the Lake and Galahad).
Others who appear to have accompanied Arthur on his forays "into the North" include St Cadog, one of Arthur's "four-and-twenty horsemen", who founded a monastery in central Scotland, and whose hagiography features several encounters with Arthur and other contemporary figures, such as Rhydderch of Dumbarton (died circa 614). Rhydderch, meanwhile, is repeatedly associated with the Merlin-figure, Myrddin Wyllt, who "went mad" at a battle fought in the Scottish Borders in 573 and then spent much of his time in the "Caledonian forest", where at least one of Arthur's battles was fought, according to a list compiled in about 829 by a Welsh monk commonly known as Nennius.
3. The early romances associate Arthur - and the Grail - with the North.
As early as 1120, Lambert, the canon of St Omer in Brittany, wrote of the "palace of the warrior Arthur" as being "in the land of the Picts" - or Scotland, as we would now know it. Lambert wrote in Latin, but used a Gaelic name for Arthur (Artuir militis).
Most mainstream accounts of "King Arthur" do not mention Lambert's testimony because it draws us away from the myth of the southern Arthur. That myth was forged by Geoffrey of Monmouth, whose account of Arthur's life and career formed part of his Historia Regum Britanniae or "History of the Kings of Britain", which he completed in about 1137. Geoffrey appears singlehandedly to have invented the legend of Arthur's birth at Tintagel in Cornwall. He also claimed that Merlin transported the "Giant's Dance" from Ireland by magic, bringing it to England where it became known as Stonehenge. Very few people take that claim seriously, and yet a surprising number are eager to take the equally unfounded story about Tintagel as Gospel. (In a later account, Geoffrey placed Merlin in the company of Taliesin, correctly identifying Myrddin Wyllt as the origin of the Merlin legend and a contemporary of the late-6th-century "Primary Chief Bard", but by then the damage had been done - those who wanted Arthur to have been "English" had the Tintagel myth to turn to, even though nobody before Geoffrey of Monmouth had mentioned it.)
Still, writers in Britain and on the Continent continued to link Arthur and his exploits with the North. Beroul, for example, whose verse romance of Tristan was composed in about 1200, stated unequivocally that Arthur and his Round Table were located at Stirling, on the River Forth in central Scotland. There was indeed a "Tristan" who was contemporary with Artur mac Aedain. His name was originally Pictish - Drust - but the Scots came to think of him as "St Drostan" and placed him in the company of St Columba (as "Drosten", he is named on a 9th-century Pictish stone at St Vigeans in Angus, not far from the scene of Artur's last battle; an early British account has "Drystan" fleeing with his lover, Esyllt, into the "Caledonian forest").
In Chretien de Troyes's version of the Peredur story - Perceval ou le conte du graal - the sword presented to the Grail knight by his uncle, the Fisher King, could only be "rehammered, retempered and repaired" at a lake beyond the River Forth. The Estoire del Saint Graal, composed in about 1230, stated that both Joseph of Arimathea, who supposedly brought the "Holy Grail" to Britain, and his son Josephus were buried in Scotland. At about the same time, one Guillaume le Clerc wrote his romance of Fergus, in which a young would-be knight encounters Arthur and his men in Galloway and then goes on a quest across much of Scotland. The Queste del Saint Graal (circa 1230) remarked that Celydoine, an ancestor of the knights Lancelot and Galahad, was "the first Christian king to hold sway over Scotland".
An oral tradition concerning Arthur continued in Scotland - and especially in the islands of the Hebrides - until the tales were finally written down in the 18th and 19th centuries. In one of these, which was recorded on the Isle of Tiree, very close to Iona, Arthur is "Chief Arthur son of Iuthar".
4. Arthur's enemies were northern.
Traditionally, Arthur fought against the Saxons, who colonised much of southern Britain in the 5th and 6th centuries AD. The term "Saxon" is still used in Welsh (Sais) and Scottish Gaelic (Sasunn) to designate an "Englishman" and "England" respectively. The term "England", however, derives not from the Saxons but from the Angles, who formed Engla land some time after they had established their kingdom of Northumberland.
The Angles did not lay claim to their first northern kingdom (Bryneich - or Bernicia, as the Angles called it) until about AD 547. They later added the kingdom of Deira (British Deywr) in 559, and together these adjacent territories on the coast of north-east England formed the Anglian kingdom of Northumberland. Forays were made into central Scotland (thus, Artur and his contemporaries fought them in Lennox, near Loch Lomomd, and at Craigmaddie Muir, north of Glasgow). By 590, though, an alliance of British and Irish chieftains had pretty much driven the Angles back into the sea. Only the treachery of a British petty-king, Morgan the Wealthy, whose power base was at the Edinburgh, caused the British resistance to collapse after the assassination of Urien of North Rheged.
Just five years later, the resurgent Angles overran much of the North. They finally conquered Edinburgh and Lothian in 638.
Between 590 and 595, or thereabouts, the invading "English" underwent an astonishing change of fortune - from being all-but wiped out in 590 to taking control of much of North Britain in 595.
Artur mac Aedain, we should remember, died in a battle fought in Angus in 594. During his lifetime, the Anglian threat had been contained, and almost eradicated, before an act of treachery led to the death of Arthur's companion, Urien, and then his own death opened the floodgates to the conquest of North Britain by the Angles. The historical circumstances therefore square with the later legends of Arthur: he sought to hold back the English, and was remarkably successful in doing so, until treachery struck. And with the death of Arthur, Britain was finished.
But the Angles were not his sole enemies. Geoffrey of Monmouth - who acknowledged that Arthur had fought battles around Dumbarton and Loch Lomond, a very long way from his supposed base in the south - also noted that there had been "Scots, Picts and Irish" ranged against Arthur in his final conflict, and that the various factions who had been brought into alliance by a treacherous British chieftain included both pagans and Christians. Geoffrey specifically stated that the "Saxons" were to be awarded with the land between the River Humber and Scotland - that is, Northumberland, the land of the Angles - in return for joining forces against Arthur.
5. Arthur's last battle was fought in the North.
We think of it as the "Battle of Camlann", and yet no contemporary references to any such battle survive. The last battle of Arthur doesn't appear to have been referred to as "Camlann" until the Middle Ages, when it was entered into the Annals of Wales as Gueith cam lann, the "Strife of Camlann".
It is usually assumed that "Camlann" is, and could only be, a Welsh place-name. This is not a reasonable assumption: the old Roman fort at Camelon, near Falkirk (just south of Stirling), is known as Camlan in Gaelic (Kemlin in Scots), and so we shouldn't suppose that cam lann was an authentic British (i.e. Brittonic) place-name.
In fact, the term cam lann translates via Anglo-Saxon - and via Lowland Scots, a derivative of the Old Germanic tongue spoken by the Angles, which had been established in southern Scotland by the 7th century - as "comb land".
Artur mac Aedain, we recall, died in 594 at a "battle of Circenn". The term circenn combines two Old Irish words, cir - meaning "comb" or "crest" - and cenn, meaning "heads". The Angus region, which was then known as Circenn, appears to have been the capital of the Miathi Picts, who seem to have modelled their appearance on the boar (Galam, a chief of the southern Picts who was almost certainly killed by Arthur in 580, bore two epithets: Cennaleth, or "Chief of Alyth", and Cennfaeladh, meaning "Shaved-Head"; he was also known as "Little-Boar", Welsh Baeddan, or "Little Tufted One", Gaelic Badan, since his head was shaved to represent the tuft, crest or "comb" of a boar).
So, Artur mac Aedain died in 594 in a battle in Circenn, the land of the "Comb-heads" or the boar-crested warriors of the Miathi Picts. His death more or less put an end to the British resistance to Anglian invasion.
The Arthur of legend died in a battle in "Comb land" or cam lann. His death more or less put an end to the British resistance to the "Saxons", or the English as they are now known.
With this in mind, we might return to the Y Gododdin poem of Aneirin, which sang of the heroes (many of them resident fixtures of the Arthurian legends) who fought so valiantly in a disastrous encounter with the Northumbrian Angles which took place not long before the year 600 and not all that far from Edinburgh. Indeed, Aneirin tells us where it happened:
Again they came into view around the Allaid,
The battle-horses and the bloody armour,
Still steadfast, still united ...
The "Allaid" (Gaelic Ailt) was the Hill of Alyth, above the River Isla in Strathmore, the great valley of Angus.
As previously stated, the earliest surviving version of Y Gododdin includes a reference to Arthur. This reference has been repeatedly mistranslated by scholars who do not want to think of Arthur as a northerner or to consider the possibility that Arthur might have been present at this disastrous battle between the Gododdin warriors of Lothian and the massed ranks of Angles, Scots, Irish and Picts. Here's the passage which mentions Arthur:
Gochore brein du ar uur
caer ceni bei ef arthur
rug ciuin uerthi ig disur ...
We can now translate this passage thus:
"Black ravens sang in praise of the hero
of Circenn. He blamed Arthur;
the dogs cursed in return for our wailing ..."
The "hero" (Welsh arwr) of "Circenn" (corrupted to caer and the genitive ceni in the transcription) was probably Arthur, who was blamed for his own death by his principle enemy whilst his black raven warriors sang their dirges over him.
As St Columba had predicted, he had "fallen in battle, slain by enemies". This battle was fought against a motley bunch of Angles, Scots, Picts and Irish, and it took place in the "comb land" (cam lann) of the "Comb-heads" (Circenn), where Arthur - surrounded by those very princes of North Britain who would follow him into the legends - was fatally wounded near the Allaid or "Hill of Alyth", the chief seat of Galam, the onetime boar-king of the Miathi.
This region is also known as Gowrie, after Gabran, the grandfather of Artur mac Aedain, who had annexed the territory in about 525. The place where Artur fell is known to this day as Arthurbank, the precise spot still being known as Arthurstone.
Southern Britain never had an Arthur, nor even a figure remotely like Artur mac Aedain.
The myth of the southern Arthur is exactly that - a myth.
The real Arthur, as all the available evidence indicates, was a northerner, active in the second half of the 6th century, and only blind prejudice stands in the way of our recognition of Artur mac Aedain as the hero he was.
Tuesday, 17 December 2013
Finding Arthur
Very exciting to see this in the Scotsman newspaper yesterday. It's a short piece about Adam Ardrey's latest Arthurian publication, Finding Arthur: The Truth Behind the Legend of the Once and Future King.
I've had some contact with Adam Ardrey in recent years - although, keen as I am to preserve my historiographical independence, we've not exactly compared notes. I read his Finding Merlin when it came out in 2007, and we've communicated once or twice since then. But we're hardly collaborators.
I stress that for a couple of reasons. First, let me quote Ardrey's words from the back cover of Finding Merlin:
"If I am right, it would appear that, for 1,500 years, those with the power to do so have presented a history that, literally, suited their book, irrespective of its divergence from the evidence, and that the stories of Arthur and Merlin which form the British foundation myth are almost entirely pieces of propaganda based on various biases. If I am right, British history for the period from the late fifth to the early seventh century stands to be rewritten."
Sounds a bit like me, doesn't it? I too have argued that propaganda and bias have dictated the retelling of the Arthurian legends through the ages - just as propaganda and bias dictate what we allowed to hear, think and believe about William Shakespeare.
What is more, though, Adam Ardrey argues in his Finding Arthur book, not only that Artur mac Aedain was the original Arthur, but that he was buried on the Isle of Iona.
So we agree on that, too.
In other words, both of us have - independently - identified a known historical prince as the original "King Arthur", and we have both tracked down his grave to the sacred royal burial isle of the Scottish kings. That's two intelligent and inquisitive individuals who have each devoted years to the subject arriving at very similar conclusions.
I posted the piece in the Scotsman newspaper (link above) to Facebook yesterday, and it was quickly shared by a very successful historical novelist. The responses were most telling.
First came the observation that a Scottish historian had received coverage in a Scottish newspaper for his theory that Arthur was Scottish. Evidently, this was all very suspicious (I pointed out that I'm an English historian with Welsh roots, and so the suggestion that only a Scot would think Arthur might have been Scottish doesn't quite stand up). What makes this kneejerk rush to judgement so interesting is that there is no basis for it. It is, in fact, a form of projection. The fact that there is no evidence whatsoever that Arthur was what the English like to think he was gets instantly spun round, becoming no other culture is allowed to claim Arthur as its own, regardless of the evidence.
I posted a few days ago about the Ossian poems, translated from the Gaelic and published by James Macpherson in the 1760s, and the English response to the evidence of a thriving, heroic Gaelic culture at a time when England didn't even exist. The response was nothing short of blind fury - a kind of spluttering outrage that the "primitives" and "savages" of the Highlands and Islands should presume to imagine that they had any pedigree, any marvellous history, for such cultural treasures belonged only to the English!!!
The same prejudice shows itself whenever the Scottish Arthur is mentioned. Without viewing the evidence, the instinctive response is: "No, he can't have been." I repeat - without viewing the evidence. So we are not dealing with considered judgements here. We are dealing with prejudice, pure and simple. The implicit racism is apparent in the suggestion that only a Scottish historian would try to place Arthur in Scotland. Even though the very first Arthur to appear in any historical record was a Scot!
There is, then, a wall of prejudice encountered by anyone who, having spent years studying and researching the evidence, concludes that there was only one viable candidate for the prestigious role of the original Arthur - and it was Artur mac Aedain, whose father was ordained as the King of the Scots by St Columba in AD 574.
It is reassuring, then, to find that others who have devoted themselves to uncovering the historical truth behind the Arthur legend have arrived at much the same conclusion as me - he was Artur mac Aedain, and he was buried on Iona. The question, then, is when will the tide turn? When will the wall of prejudice crumble in the face of the evidence? When will the English finally admit that they have no claim at all to Arthur?
(I don't include the Welsh here because Arthur was British, and Welsh-speaking Britain extended at least as far north as the River Forth in his day; there are no grounds for presuming that, if Arthur was the son of a Scottish king, then he couldn't have been Welsh: rather, that argument is based on a misunderstanding of the geopolitics of 6th-century Britain.)
I'm tempted to post, over the next few days, a number of indisputable facts about Arthur. These are not assumptions, but genuine facts. And they all point in one direction, and one direction only.
The English might fight tooth and nail to cling to their myth of King Arthur. But there can be no reasonable doubt as to who the original Arthur was.
Unless you're determined to ignore the evidence, that is.
I've had some contact with Adam Ardrey in recent years - although, keen as I am to preserve my historiographical independence, we've not exactly compared notes. I read his Finding Merlin when it came out in 2007, and we've communicated once or twice since then. But we're hardly collaborators.
I stress that for a couple of reasons. First, let me quote Ardrey's words from the back cover of Finding Merlin:
"If I am right, it would appear that, for 1,500 years, those with the power to do so have presented a history that, literally, suited their book, irrespective of its divergence from the evidence, and that the stories of Arthur and Merlin which form the British foundation myth are almost entirely pieces of propaganda based on various biases. If I am right, British history for the period from the late fifth to the early seventh century stands to be rewritten."
Sounds a bit like me, doesn't it? I too have argued that propaganda and bias have dictated the retelling of the Arthurian legends through the ages - just as propaganda and bias dictate what we allowed to hear, think and believe about William Shakespeare.
What is more, though, Adam Ardrey argues in his Finding Arthur book, not only that Artur mac Aedain was the original Arthur, but that he was buried on the Isle of Iona.
So we agree on that, too.
In other words, both of us have - independently - identified a known historical prince as the original "King Arthur", and we have both tracked down his grave to the sacred royal burial isle of the Scottish kings. That's two intelligent and inquisitive individuals who have each devoted years to the subject arriving at very similar conclusions.
I posted the piece in the Scotsman newspaper (link above) to Facebook yesterday, and it was quickly shared by a very successful historical novelist. The responses were most telling.
First came the observation that a Scottish historian had received coverage in a Scottish newspaper for his theory that Arthur was Scottish. Evidently, this was all very suspicious (I pointed out that I'm an English historian with Welsh roots, and so the suggestion that only a Scot would think Arthur might have been Scottish doesn't quite stand up). What makes this kneejerk rush to judgement so interesting is that there is no basis for it. It is, in fact, a form of projection. The fact that there is no evidence whatsoever that Arthur was what the English like to think he was gets instantly spun round, becoming no other culture is allowed to claim Arthur as its own, regardless of the evidence.
I posted a few days ago about the Ossian poems, translated from the Gaelic and published by James Macpherson in the 1760s, and the English response to the evidence of a thriving, heroic Gaelic culture at a time when England didn't even exist. The response was nothing short of blind fury - a kind of spluttering outrage that the "primitives" and "savages" of the Highlands and Islands should presume to imagine that they had any pedigree, any marvellous history, for such cultural treasures belonged only to the English!!!
The same prejudice shows itself whenever the Scottish Arthur is mentioned. Without viewing the evidence, the instinctive response is: "No, he can't have been." I repeat - without viewing the evidence. So we are not dealing with considered judgements here. We are dealing with prejudice, pure and simple. The implicit racism is apparent in the suggestion that only a Scottish historian would try to place Arthur in Scotland. Even though the very first Arthur to appear in any historical record was a Scot!
There is, then, a wall of prejudice encountered by anyone who, having spent years studying and researching the evidence, concludes that there was only one viable candidate for the prestigious role of the original Arthur - and it was Artur mac Aedain, whose father was ordained as the King of the Scots by St Columba in AD 574.
It is reassuring, then, to find that others who have devoted themselves to uncovering the historical truth behind the Arthur legend have arrived at much the same conclusion as me - he was Artur mac Aedain, and he was buried on Iona. The question, then, is when will the tide turn? When will the wall of prejudice crumble in the face of the evidence? When will the English finally admit that they have no claim at all to Arthur?
(I don't include the Welsh here because Arthur was British, and Welsh-speaking Britain extended at least as far north as the River Forth in his day; there are no grounds for presuming that, if Arthur was the son of a Scottish king, then he couldn't have been Welsh: rather, that argument is based on a misunderstanding of the geopolitics of 6th-century Britain.)
I'm tempted to post, over the next few days, a number of indisputable facts about Arthur. These are not assumptions, but genuine facts. And they all point in one direction, and one direction only.
The English might fight tooth and nail to cling to their myth of King Arthur. But there can be no reasonable doubt as to who the original Arthur was.
Unless you're determined to ignore the evidence, that is.
Labels:
Arthur,
Arthur's Grave,
Iona,
Merlin,
Ossian,
Scotland,
Shakespeare,
St Columba
Saturday, 14 December 2013
Ossian: Culture and Prejudice
It's taken me a while, but I've finally got round to researching the poems of Ossian.
"So what?" I hear you cry. Well, each to his own.
Let me fill you in.
James Macpherson was born in the Scottish Highlands in 1736. A native Gaelic speaker, he wasn't quite ten years old when the Jacobite rebellion under Bonnie Prince Charlie came to a terrible end at Culloden, not so very far from where Macpherson had grown up.
There had been prominent rebels in his family - including Cluny Macpherson, who makes a colourful appearance in Robert Louis Stevenson's Kidnapped.
James Macpherson was clever, quick-witted and well-educated. In 1760, he published Fragments of Ancient Poetry - Collected in the Highlands of Scotland and Translated from the Gaelic or Erse Language. These Fragments introduced the world to the ancient world of Fingal (Fionn mac Cumhail), his son Ossian and grandson Oscar (yes, Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde was named after him). They were an instant success.
The Scottish literati then raised the funds for Macpherson to make a research trip to the Highlands and Islands with a view to collecting more scraps of traditional Gaelic verse, either orally or in manuscript form. The result of this expedition was Fingal: An Ancient Epic Poem in Sixth Books.
Macpherson had made his name. His Ossianic collections were the talk of Europe and beyond. Thomas Jefferson considered them his favourite books; Napoleon Buonaparte never went into battle without a copy to hand, and Goethe was hugely inspired by the Gaelic epic. Romanticism - the predominant aesthetic movement of the 19th century - owed a great deal to Macpherson's work. Felix Mendelssohn made a sort of pilgrimage to the Western Isles after reading the Ossian poems, and was inspired to write his stirring Hebridean Overture, although sea-sickness had prevented him from viewing "Fingal's Cave" on Staffa.
But the English hated the Ossian poems. Led by the bullish figure of Dr Samuel Johnson, the southern establishment poured scorn on Macpherson's efforts. Johnson demanded that Macpherson reveal his sources and produce the Gaelic manuscripts from which he had drawn his translations. As far as Dr Johnson was concerned, the whole thing was a hoax. There were no historic manuscripts concerning Fingal. Macpherson had made the whole thing up.
Not true. There were mentions of Fingal and Ossian in historical manuscripts, and subsequent research has shown that Macpherson did indeed base his work on original, authentic Gaelic poetry. And yet Macpherson - and Ossian - are little known today. So one could say that Dr Johnson and his English crew succeeded. They threw enough mud for some of it to stick.
Why, though? Why was it so important to Dr Johnson, and others like him, to undermine James Macpherson's achievements?
At the time, Gaelic society was in decline. It has since been sentimentalised and fetishised, but first its roots had to be torn up and the culture pretty much destroyed.
The crowns of England and Scotland had been united in 1603 under James Stuart, the sixth King James of Scotland (but usually referred to as James I - his English designation). It was not until 1707, though, that the Scots were bribed and bullied into accepting an Act of Union with England. This was very much to England's benefit - it meant that France lost a valuable ally north of England's border - and very much to Scotland's disadvantage. Indeed, the Union was detested on both sides of the English-Scottish border.
The last serious attempt to break up the Union, or to restore the Stuart line to the throne (if only in Scotland), came when Charles Edward Stuart landed with seven men in the Outer Hebrides. It ended with the disaster at Culloden in 1746. The English, under the "Butcher" Duke of Cumberland, a son of the reigning Hanoverian king, raped and massacred their way through the Highlands. The wearing of Scottish dress (the tartan kilt) was banned, as was the possession of weapons.
Before too long, the time-honoured clan system was breaking down. The clan chiefs were replaced by landlords, who held no sense of responsibility to the inhabitants of the Highlands. Sheep were more profitable than people, and so houses were burned down, possessions confiscated, and thousands of men, women and children herded into overcrowded vessels to make long and painful journeys to the farthest flung corners of the Empire. The Highlands became a wasteland, an exclusive playground for the very rich.
With the determined annihilation of Gaelic culture well and truly underway, Macpherson's publications were a bit of a problem. They demonstrated that the culture of the Highlands (and, in particular, the west) was truly ancient. Some even considered the Ossianic poems comparable with the works of Homer and Virgil. It was as if, just as the English and their supporters in the Lowlands were systematically crushing Highland society, a Highlander had come along and shown that the Gaels had a culture and tradition which far surpassed anything that any Englishman could boast of.
To men like Dr Samuel Johnson, the Scots were primitives, a ragged bunch of scheming savages. English racism - never very far from the surface - was making exaggerated and hysterical claims about Scots migrating en masse to London and taking jobs, houses and women (sound familiar?). South of the border, words like "Scot" and "Scottish" were a form of abuse
Things worsened when John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, became the first Scottish prime minister of Great Britain. Bute was a favourite of King George III (the "mad" one), but he bore the hated name of Stuart, and he was a Scot - so the English loathed him. Macpherson had dedicated his Ossianic works to Lord Bute, which gave Englishmen like Dr Johnson another reason to attack Macpherson and his discoveries.
There is much that is magnificent in the Ossianic poems, even if Macpherson had embellished the original Gaelic verses he collected throughout the Highlands and Islands. They give flashes of insight into a heroic society and glimpses of life at a time when Christianity was just beginning to establish itself (there are no Christian references in the poems). What is more, they offer proof that the western seaboard of Scotland was home to a remarkable culture before the invading Angles and Saxons converged to form England. They deserve to be better known. No; more than that - they are part of the ancestral heritage of the British Isles, and it was a cultural atrocity on the part of the English to try to wipe them from the record and to impugn the reputation of the man who collected, translated and published them.
And there's more. The Ossian poems give us an insight into the society of Arthur. Yes, Arthur. That Arthur - the one the English falsely insist on calling "King Arthur".
English prejudices run deep. If they can't have Arthur all to themselves, then no one can.
The real, original, historical Arthur was a Scottish prince. There never was an "English" King Arthur, and no evidence at all exists for an Arthur in the south. He was a North Briton, and his world was the world of Fingal and Ossian and Oscar.
But just as English scholars refused to allow the Scots to have an ancient, heroic culture - refused even to let them have a language, or a home - so English commentators continue to tell lies about Arthur, if only to prevent the world from knowing that his father was King of the Scots.
One day - let us hope - the Ossianic poems will take their place alongside the native tales of Arthur and his heroes (which continually refer to "the North"). Macpherson will be honoured as he should be: as the man who preserved these traces of authentic tradition and was cruelly satirised and savagely lambasted for doing so. The crimes committed against the culture and people of the Highlands will be fully recognised and acknowledged. And it will be possible to investigate and celebrate the genuine Arthur of history, rather than the insipid legendary concoction foisted upon us by the propagandists of the south.
"So what?" I hear you cry. Well, each to his own.
Let me fill you in.
James Macpherson was born in the Scottish Highlands in 1736. A native Gaelic speaker, he wasn't quite ten years old when the Jacobite rebellion under Bonnie Prince Charlie came to a terrible end at Culloden, not so very far from where Macpherson had grown up.
There had been prominent rebels in his family - including Cluny Macpherson, who makes a colourful appearance in Robert Louis Stevenson's Kidnapped.
James Macpherson was clever, quick-witted and well-educated. In 1760, he published Fragments of Ancient Poetry - Collected in the Highlands of Scotland and Translated from the Gaelic or Erse Language. These Fragments introduced the world to the ancient world of Fingal (Fionn mac Cumhail), his son Ossian and grandson Oscar (yes, Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde was named after him). They were an instant success.
The Scottish literati then raised the funds for Macpherson to make a research trip to the Highlands and Islands with a view to collecting more scraps of traditional Gaelic verse, either orally or in manuscript form. The result of this expedition was Fingal: An Ancient Epic Poem in Sixth Books.
Macpherson had made his name. His Ossianic collections were the talk of Europe and beyond. Thomas Jefferson considered them his favourite books; Napoleon Buonaparte never went into battle without a copy to hand, and Goethe was hugely inspired by the Gaelic epic. Romanticism - the predominant aesthetic movement of the 19th century - owed a great deal to Macpherson's work. Felix Mendelssohn made a sort of pilgrimage to the Western Isles after reading the Ossian poems, and was inspired to write his stirring Hebridean Overture, although sea-sickness had prevented him from viewing "Fingal's Cave" on Staffa.
But the English hated the Ossian poems. Led by the bullish figure of Dr Samuel Johnson, the southern establishment poured scorn on Macpherson's efforts. Johnson demanded that Macpherson reveal his sources and produce the Gaelic manuscripts from which he had drawn his translations. As far as Dr Johnson was concerned, the whole thing was a hoax. There were no historic manuscripts concerning Fingal. Macpherson had made the whole thing up.
Not true. There were mentions of Fingal and Ossian in historical manuscripts, and subsequent research has shown that Macpherson did indeed base his work on original, authentic Gaelic poetry. And yet Macpherson - and Ossian - are little known today. So one could say that Dr Johnson and his English crew succeeded. They threw enough mud for some of it to stick.
Why, though? Why was it so important to Dr Johnson, and others like him, to undermine James Macpherson's achievements?
At the time, Gaelic society was in decline. It has since been sentimentalised and fetishised, but first its roots had to be torn up and the culture pretty much destroyed.
The crowns of England and Scotland had been united in 1603 under James Stuart, the sixth King James of Scotland (but usually referred to as James I - his English designation). It was not until 1707, though, that the Scots were bribed and bullied into accepting an Act of Union with England. This was very much to England's benefit - it meant that France lost a valuable ally north of England's border - and very much to Scotland's disadvantage. Indeed, the Union was detested on both sides of the English-Scottish border.
The last serious attempt to break up the Union, or to restore the Stuart line to the throne (if only in Scotland), came when Charles Edward Stuart landed with seven men in the Outer Hebrides. It ended with the disaster at Culloden in 1746. The English, under the "Butcher" Duke of Cumberland, a son of the reigning Hanoverian king, raped and massacred their way through the Highlands. The wearing of Scottish dress (the tartan kilt) was banned, as was the possession of weapons.
Before too long, the time-honoured clan system was breaking down. The clan chiefs were replaced by landlords, who held no sense of responsibility to the inhabitants of the Highlands. Sheep were more profitable than people, and so houses were burned down, possessions confiscated, and thousands of men, women and children herded into overcrowded vessels to make long and painful journeys to the farthest flung corners of the Empire. The Highlands became a wasteland, an exclusive playground for the very rich.
With the determined annihilation of Gaelic culture well and truly underway, Macpherson's publications were a bit of a problem. They demonstrated that the culture of the Highlands (and, in particular, the west) was truly ancient. Some even considered the Ossianic poems comparable with the works of Homer and Virgil. It was as if, just as the English and their supporters in the Lowlands were systematically crushing Highland society, a Highlander had come along and shown that the Gaels had a culture and tradition which far surpassed anything that any Englishman could boast of.
To men like Dr Samuel Johnson, the Scots were primitives, a ragged bunch of scheming savages. English racism - never very far from the surface - was making exaggerated and hysterical claims about Scots migrating en masse to London and taking jobs, houses and women (sound familiar?). South of the border, words like "Scot" and "Scottish" were a form of abuse
Things worsened when John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, became the first Scottish prime minister of Great Britain. Bute was a favourite of King George III (the "mad" one), but he bore the hated name of Stuart, and he was a Scot - so the English loathed him. Macpherson had dedicated his Ossianic works to Lord Bute, which gave Englishmen like Dr Johnson another reason to attack Macpherson and his discoveries.
There is much that is magnificent in the Ossianic poems, even if Macpherson had embellished the original Gaelic verses he collected throughout the Highlands and Islands. They give flashes of insight into a heroic society and glimpses of life at a time when Christianity was just beginning to establish itself (there are no Christian references in the poems). What is more, they offer proof that the western seaboard of Scotland was home to a remarkable culture before the invading Angles and Saxons converged to form England. They deserve to be better known. No; more than that - they are part of the ancestral heritage of the British Isles, and it was a cultural atrocity on the part of the English to try to wipe them from the record and to impugn the reputation of the man who collected, translated and published them.
And there's more. The Ossian poems give us an insight into the society of Arthur. Yes, Arthur. That Arthur - the one the English falsely insist on calling "King Arthur".
English prejudices run deep. If they can't have Arthur all to themselves, then no one can.
The real, original, historical Arthur was a Scottish prince. There never was an "English" King Arthur, and no evidence at all exists for an Arthur in the south. He was a North Briton, and his world was the world of Fingal and Ossian and Oscar.
But just as English scholars refused to allow the Scots to have an ancient, heroic culture - refused even to let them have a language, or a home - so English commentators continue to tell lies about Arthur, if only to prevent the world from knowing that his father was King of the Scots.
One day - let us hope - the Ossianic poems will take their place alongside the native tales of Arthur and his heroes (which continually refer to "the North"). Macpherson will be honoured as he should be: as the man who preserved these traces of authentic tradition and was cruelly satirised and savagely lambasted for doing so. The crimes committed against the culture and people of the Highlands will be fully recognised and acknowledged. And it will be possible to investigate and celebrate the genuine Arthur of history, rather than the insipid legendary concoction foisted upon us by the propagandists of the south.
Friday, 8 November 2013
The Grail - CAMLANN
Chapter 10 of The Grail; Relic of an Ancient Religion - entitled "Camlann" - is now up on the Moon Books blog!
I've written about the Battle of Camlann before on this blog, and with The Grail I have been able to put the fruits of yet more research out there. I have finally (I believe) tracked down the original meaning of cam lann - which is how the place-name first appears - and it confirms that Artuir mac Aedain was the one and only Arthur of history.
There is quite a lot more detail given of the final battle in this chapter, especially in terms of topography (what the sources tell us about the scene and where those references show up on today's map), leaving precious little room for doubt as to where Arthur's last battle was fought. And all this builds up to a revelation which will be made in the next chapter:
The Grail can still be seen in the immediate vicinity of Arthur's last battle!
That chapter will be up in about a month's time. I'll let you know.
I've written about the Battle of Camlann before on this blog, and with The Grail I have been able to put the fruits of yet more research out there. I have finally (I believe) tracked down the original meaning of cam lann - which is how the place-name first appears - and it confirms that Artuir mac Aedain was the one and only Arthur of history.
There is quite a lot more detail given of the final battle in this chapter, especially in terms of topography (what the sources tell us about the scene and where those references show up on today's map), leaving precious little room for doubt as to where Arthur's last battle was fought. And all this builds up to a revelation which will be made in the next chapter:
The Grail can still be seen in the immediate vicinity of Arthur's last battle!
That chapter will be up in about a month's time. I'll let you know.
Labels:
Arthur,
Artuir mac Aedain,
Camlan,
Grail,
Moon Books
Thursday, 24 October 2013
Kitchen Witchcraft
Witch. It's such a troublesome word, isn't it? So many negative connotations.
Centuries of misinformation, prejudice and propaganda turned the very notion of "witchcraft" into something hideous and fearful. We see similar processes at work today - in the United States, for example, where a positive word like "liberal" (meaning generous, open-minded, and inclined towards favouring individual liberty) has been turned into a political insult. Whenever we see something like that happening - wherever a perfectly good word denoting a perfectly decent political or religious stance is transformed into a term of abuse, becoming a sort of catch-all "bogeyman" for the majority to fear and loathe - we have to question the motives of those who drive that semantic change.
One way or another, witchcraft is an extremely ancient pursuit. It's difficult to separate "witchcraft" from its companion concept, "paganism". Both have been enjoying something of a resurgence, lately - and, overall, that's a good thing, because this represents a return of sorts to an older and more natural way of doing things.
The term "pagan" means, simply, country-dweller (paganus). While the more elaborate cults flourished in the cities of the ancient world, those cities were utterly dependent on rural communities to provide the food for their markets and their tables. And those rural communities remained in touch with the processes of agriculture, the cycle of the seasons, the hardwork, care, attention and - yes - hope which are all necessary if we are to enjoy ample harvests.
Typically, city-dwellers came to look down on the country-folk as rural idiots, even though the urbanites were dependent on them for the absolute necessities. The country-folk knew that the weather mattered. They knew that water was essential; anything that polluted a water-source was a huge threat. Better to keep the water-spirits happy. And to do whatever you could to secure good weather. And cherish the plants and animals that provide for us.
Various rituals and forms of worship evolved in order to make farming - that most essential of occupations - as successful as it could reasonably be. We do much the same these days, only we do it all wrong: pesticides, intensive farming, GM crops are all signs of a system under immense strain. We have forgotten how to farm, and keep trying to make it more "efficient", and to compensate for the damage we did previously, by piling on the pressure.
What the pagans of old knew - and what others, like the Findhorn Community, have discovered since - is that you can't bully nature. You can try, but it'll backfire on you. You have to coax it, work with it, be nice to it. The whole thing is a transaction between us, the human community, and the multitudinous spirits which inhabit the natural world. If we are good to them, then they'll probably be good to us. If we ignore them, and then ruin their habitats, they'll make our lives more difficult.
So that's paganism - the cautious, conscientious and frequently joyous process of interacting with the natural environment in the hope of securing positive outcomes. And every community had those (male or female) who were just a little bit more expert at this sort of thing than the rest of us. They understood which plants were good for treating which ailments of the body, mind or spirit. Though most of us lived close to nature - right in amongst it, if you like - they lived as part of nature, doing the deals that were needed to be done. To be more precise, such people worked with the spiritual side of nature, including past members of the human community. If a priest intercedes between man and God, the witch interceded between man and the gods.
Rachel Patterson lives in a city. But she also knows that her home and garden benefit from a little care and attention, on both the material and spiritual levels. A clean kitchen is one thing; a kitchen that is in tune with the seasons and used as a place in which to celebrate the seasonal round - the systole and diastole of winter and summer - is not just clean: it is happy.
Rachel's book, Kitchen Witchcraft: Crafts of a Kitchen Witch - part of the Moon Books "Pagan Portals" series - is delightful. She writes with a great sense of fun and real love for the world around us. And the book serves as a sort of primer, a very gentle but effective introduction to the ideas and principles of contemporary paganism. Forget about magical oils made out of bats' wings - today, we use essential oils. They make our candles smell nice.
What really works about this book is that it fits in so comfortably with the modern obsession with home improvement and that all important do-it-yourself ethos. Rachel acknowledges, early on, that the kitchen (or hearth) is the heart of the home. It is where our food is prepared and cooked - and often eaten. It is a personal space (most cooks like to work alone) and a convivial space, a place of conversations, hearts-to-hearts. No other room is quite like it. And, like the hearth of old, it needs to look and smell and feel special. We need, in effect, to love our kitchens - and to show that we love them. We need to personalise them: not out of a catalogue, but with our own arts and crafts.
There are blessings in this book, and meditations, but nothing remotely "witchy" in the sense of diabolical (and why should there be? - who wants bad spirits running amok in their kitchen?). As with so much that is useful in the pagan world, much of it is just sound psychological common sense, comprising various activities which can put you in a better mood and improve the mood of your environment (the two go hand in hand). At the same time, Rachel Patterson provides quick rundowns of some of the basic elements of the pagan worldview - the regular festivals, the essential elements - and works these into her simple "recipes" for a happy home.
Anyone who is offended by anything in Rachel's book has real problems. Only the worst kind of superstition, fostered by indoctrination, could view Kitchen Witchcraft as a menace to Creation. But then, that indoctrination is so often applied by mindsets that are addicted to suffering. Rachel Patterson, in her lovely, short, joyful book, implies that suffering might be natural, but it is not to be encouraged. The kitchen should be a place of life, not death. A few flowers, candles, stones and shells are unlikely to do any harm, and if they improve our relationships with ourselves, with our kitchens and with the world outside, then what's wrong with that? We need more of this sort of thing.
Reading the book reminded me of the Pagan Pride festival in Nottingham, this past August. It was a lovely event, with a pronounced fancy-dress feel (including a rather glamorous Robin and Marion duo), and amounted to little more than a relaxed and good-humoured celebration of life.
After I had given a talk on "Arthur and the Grail", we made our way out of the park, walking behind two elderly ladies who had dressed up as witches. Lovely homemade cloaks and pointy hats. And I was really touched to see that these two women were having fun. They had been allowed to announce, in public, "Yes, we are witches. We belong to a most ancient tradition."
Were they evil? I doubt that very much. They were probably heading home for a cup of tea. And I'd like to think that their kitchens are sacred spaces, where nourishment is lovingly prepared.
Their playfulness, their honesty about themselves, and the fact that - thankfully, at long last - it is possible, once again, to admit that you have a relationship with the earth, with water, with air, and with fire, and that you can only be happy when working with these elements to achieve balance in your life (and really delicious cakes) ... that is what I was reminded of when reading Rachel Patterson's book.
Don't get hung up on words like "witch" or "pagan". We could all do with a little more magic in our lives - and a good place to start looking for it is in Rachel Patterson's little book of Kitchen Witchcraft.
Centuries of misinformation, prejudice and propaganda turned the very notion of "witchcraft" into something hideous and fearful. We see similar processes at work today - in the United States, for example, where a positive word like "liberal" (meaning generous, open-minded, and inclined towards favouring individual liberty) has been turned into a political insult. Whenever we see something like that happening - wherever a perfectly good word denoting a perfectly decent political or religious stance is transformed into a term of abuse, becoming a sort of catch-all "bogeyman" for the majority to fear and loathe - we have to question the motives of those who drive that semantic change.
One way or another, witchcraft is an extremely ancient pursuit. It's difficult to separate "witchcraft" from its companion concept, "paganism". Both have been enjoying something of a resurgence, lately - and, overall, that's a good thing, because this represents a return of sorts to an older and more natural way of doing things.
The term "pagan" means, simply, country-dweller (paganus). While the more elaborate cults flourished in the cities of the ancient world, those cities were utterly dependent on rural communities to provide the food for their markets and their tables. And those rural communities remained in touch with the processes of agriculture, the cycle of the seasons, the hardwork, care, attention and - yes - hope which are all necessary if we are to enjoy ample harvests.
Typically, city-dwellers came to look down on the country-folk as rural idiots, even though the urbanites were dependent on them for the absolute necessities. The country-folk knew that the weather mattered. They knew that water was essential; anything that polluted a water-source was a huge threat. Better to keep the water-spirits happy. And to do whatever you could to secure good weather. And cherish the plants and animals that provide for us.
Various rituals and forms of worship evolved in order to make farming - that most essential of occupations - as successful as it could reasonably be. We do much the same these days, only we do it all wrong: pesticides, intensive farming, GM crops are all signs of a system under immense strain. We have forgotten how to farm, and keep trying to make it more "efficient", and to compensate for the damage we did previously, by piling on the pressure.
What the pagans of old knew - and what others, like the Findhorn Community, have discovered since - is that you can't bully nature. You can try, but it'll backfire on you. You have to coax it, work with it, be nice to it. The whole thing is a transaction between us, the human community, and the multitudinous spirits which inhabit the natural world. If we are good to them, then they'll probably be good to us. If we ignore them, and then ruin their habitats, they'll make our lives more difficult.
So that's paganism - the cautious, conscientious and frequently joyous process of interacting with the natural environment in the hope of securing positive outcomes. And every community had those (male or female) who were just a little bit more expert at this sort of thing than the rest of us. They understood which plants were good for treating which ailments of the body, mind or spirit. Though most of us lived close to nature - right in amongst it, if you like - they lived as part of nature, doing the deals that were needed to be done. To be more precise, such people worked with the spiritual side of nature, including past members of the human community. If a priest intercedes between man and God, the witch interceded between man and the gods.
Rachel Patterson lives in a city. But she also knows that her home and garden benefit from a little care and attention, on both the material and spiritual levels. A clean kitchen is one thing; a kitchen that is in tune with the seasons and used as a place in which to celebrate the seasonal round - the systole and diastole of winter and summer - is not just clean: it is happy.
Rachel's book, Kitchen Witchcraft: Crafts of a Kitchen Witch - part of the Moon Books "Pagan Portals" series - is delightful. She writes with a great sense of fun and real love for the world around us. And the book serves as a sort of primer, a very gentle but effective introduction to the ideas and principles of contemporary paganism. Forget about magical oils made out of bats' wings - today, we use essential oils. They make our candles smell nice.
What really works about this book is that it fits in so comfortably with the modern obsession with home improvement and that all important do-it-yourself ethos. Rachel acknowledges, early on, that the kitchen (or hearth) is the heart of the home. It is where our food is prepared and cooked - and often eaten. It is a personal space (most cooks like to work alone) and a convivial space, a place of conversations, hearts-to-hearts. No other room is quite like it. And, like the hearth of old, it needs to look and smell and feel special. We need, in effect, to love our kitchens - and to show that we love them. We need to personalise them: not out of a catalogue, but with our own arts and crafts.
There are blessings in this book, and meditations, but nothing remotely "witchy" in the sense of diabolical (and why should there be? - who wants bad spirits running amok in their kitchen?). As with so much that is useful in the pagan world, much of it is just sound psychological common sense, comprising various activities which can put you in a better mood and improve the mood of your environment (the two go hand in hand). At the same time, Rachel Patterson provides quick rundowns of some of the basic elements of the pagan worldview - the regular festivals, the essential elements - and works these into her simple "recipes" for a happy home.
Anyone who is offended by anything in Rachel's book has real problems. Only the worst kind of superstition, fostered by indoctrination, could view Kitchen Witchcraft as a menace to Creation. But then, that indoctrination is so often applied by mindsets that are addicted to suffering. Rachel Patterson, in her lovely, short, joyful book, implies that suffering might be natural, but it is not to be encouraged. The kitchen should be a place of life, not death. A few flowers, candles, stones and shells are unlikely to do any harm, and if they improve our relationships with ourselves, with our kitchens and with the world outside, then what's wrong with that? We need more of this sort of thing.
Reading the book reminded me of the Pagan Pride festival in Nottingham, this past August. It was a lovely event, with a pronounced fancy-dress feel (including a rather glamorous Robin and Marion duo), and amounted to little more than a relaxed and good-humoured celebration of life.
After I had given a talk on "Arthur and the Grail", we made our way out of the park, walking behind two elderly ladies who had dressed up as witches. Lovely homemade cloaks and pointy hats. And I was really touched to see that these two women were having fun. They had been allowed to announce, in public, "Yes, we are witches. We belong to a most ancient tradition."
Were they evil? I doubt that very much. They were probably heading home for a cup of tea. And I'd like to think that their kitchens are sacred spaces, where nourishment is lovingly prepared.
Their playfulness, their honesty about themselves, and the fact that - thankfully, at long last - it is possible, once again, to admit that you have a relationship with the earth, with water, with air, and with fire, and that you can only be happy when working with these elements to achieve balance in your life (and really delicious cakes) ... that is what I was reminded of when reading Rachel Patterson's book.
Don't get hung up on words like "witch" or "pagan". We could all do with a little more magic in our lives - and a good place to start looking for it is in Rachel Patterson's little book of Kitchen Witchcraft.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)